If you’ve ever experienced delays, hitches, or couldn’t get the optimum multiplayer gaming performance despite having a high-speed internet connection, you are familiar with data packet loss. Well, you may not know the exact term but suffer from it, and you have to find out how to fix packet loss in your network.
Packet loss happens when one or more packets of data can’t reach their destination because of network congestion, faulty hardware, security breaches, or any other possible network issues. Whatever the reason behind this intolerable connectivity disruption, no worries, you can find a solution and resolve it yourself. In this blog, we are talking about what packet loss is, why it happens, and what measures you should take to fix or prevent network packet loss.
What is Packet Loss in Networking?

Packet loss in networking occurs when data packets fail to reach their intended destination within a network. Imagine sending a letter only to discover parts of it mysteriously vanished in transit. Similarly, when exchanging data, information travels in small units known as packets. Each packet carries a portion of the data and is directed to its destination. When one or more packets go astray, that’s packet loss.
Errors during data transmission, particularly in wireless networks or during periods of network congestion, can trigger packet loss. Real-time applications like streaming media and online games are significantly impacted by packet loss, as it affects the user’s quality of experience. From downloading files to engaging in video calls, every online activity involves the exchange of crucial packets. When these packets fail to reach their destination, users may experience disruptions, leading to slowed services or, in severe cases, loss of connectivity.
Packet loss can occur due to various reasons, including hardware failure or issues with the connection itself. It manifests as incomplete data sets and malfunctions, slowing streaming capabilities and buffering. Emails, for instance, commonly break into packets such as header, payload, and trailer. If a recipient receives the header and trailer but not the payload, it’s likely due to packet loss.
Symptoms of Packet Loss
Before diagnosing and fixing network lag, it’s essential to recognize the signs of packet loss. Various symptoms indicate whether packet loss is the reason behind the issue. These symptoms are often specific to particular applications, providing clues to identify packet loss scenarios.
In online gaming, packet loss manifests as erratic or choppy movements during crucial network-dependent events. Players may encounter disruptions in the game’s flow, rendering it unplayable due to inconsistent data transmission. Additionally, packet loss can cause anomalies such as timeouts and irregular counters, rendering certain actions ineffective and introducing unexpected outcomes, leading to a frustrating gaming experience.
In telecommunications, high levels of packet loss can produce an irritating ‘robotic’ effect on voices during calls. Stuttering voices make conversations challenging and adversely impact the overall quality of voice communication.
Similarly, in video communications, packet loss may result in frozen frames and stuttering behavior, disrupting the visual clarity of the video and hindering the fluidity of the conversation. These visual disruptions not only affect the clarity of the video but also diminish the effectiveness of conveying information.
Why Packet Loss Happen?
You already realize the significance of packet loss on network performance, don’t you? Let’s now identify the possible reasons behind this connectivity disruption before diving into the impacts and how to fix packet loss.
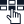
1. Network Congestion:
During peak traffic, data packets may experience delays or get dropped, similar to rush hour on a congested highway. Routers may discard packets to alleviate congestion, especially over greater distances between network points.
Modern software attempts to address this by resending lost packets or adjusting transfer speeds. In corporate settings, congestion often occurs when numerous users engage in bandwidth-intensive activities. Efficient bandwidth management is vital for smooth data transmission.
2. Faulty Network Hardware:
Damaged cables, outdated routers, or faulty network devices disrupt smooth packet flow, impacting overall network performance. Aging or outdated hardware, including firewalls, routers, switches, and endpoints like smartphones and laptops, can cause packet loss due to power limitations or bottlenecks.
Regular updates and expansion of network infrastructure are crucial for avoiding packet loss. Newer equipment comes with updated firmware, addressing vulnerabilities and improving functionality to prevent packet loss.
3. Software Bugs:
Unexpected behaviors, like dropped or delayed packets, stem from bugs in network software, firmware, or operating systems. Older software versions often harbor bugs, disrupting file transmission and causing packet loss. Unchecked bugs disrupt network performance, requiring system reboots or patches.
4. Overloaded Devices:
When many online services and apps run simultaneously, devices and networks can become overloaded. Packets may reach their destinations, but the weakened network struggles to process and transmit them efficiently. Devices often have buffers to hold packets temporarily, but these can quickly become overwhelmed, resulting in dropped packets.
5. Security Breaches:
Firewalls or intrusion detection systems may unintentionally block or filter certain packets, causing packet loss due to misconfigurations or overly strict security settings. Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks can flood the network, overwhelming resources and resulting in packet loss, requiring timely detection and response.
Packet drop attacks, where hackers tamper with routers to drop packets, are a growing concern. Implementing security measures like firewall optimization and anti-hacker software can mitigate DDoS attacks, but detecting unusual packet loss rates may indicate a security breach. Monitoring network traffic for unfamiliar activity and sluggish performance can help detect and address security threats, ensuring network integrity and minimizing packet loss.
6. Improper Network Configuration:
Faulty network configurations are a significant cause of packet loss. A single misconfiguration in a switch can trigger network loops, disrupting the entire system. As companies undergo mergers or asset divestments, and IT staff positions become outsourced, network configurations may be neglected.
Aging network equipment may struggle to support modern network management protocols like network automation and SD-WAN. These issues highlight the importance of proper network configuration maintenance to prevent packet loss. Updating equipment and implementing effective network management strategies can reduce configuration-related packet loss.
Impact of Packet Loss on Network Performance

Packet loss significantly impacts network performance and operational efficiency. It disrupts data flow and increases latency, particularly affecting real-time applications like video streaming and VoIP, resulting in compromised user experiences. Here are some of the negative impacts packet loss has on our daily communication—
- Communication Disruptions: Packet loss causes interruptions in real-time applications like VoIP, resulting in jittery audio and video.
- Reduced Data Transfer Speed: Retransmitting lost packets slows down data transfer rates, affecting overall throughput.
- Security Risks: Packet loss can create vulnerabilities, providing opportunities for cyber attacks and compromising encrypted data.
- Increased Latency: Packet loss contributes to higher latency, causing delays in data transmission and response times.
- Incomplete Data Transmission: Severe packet loss leads to incomplete transmission, resulting in missing or corrupted files and messages.
- Service Interruptions: Packet loss disrupts streaming, online gaming, and other real-time applications, impacting user experiences.
In addition, the impact of packet loss is different depending on whether it’s a TCP/IP or UDP protocol:
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP): In TCP/IP, lost packets are resent automatically to maintain data flow. This process, detailed in RFCs 3366 and 2988, ensures continuity. TCP’s congestion control, outlined in RFC 2581, prevents data traffic jams. Despite this effort, packet retransmission can slow down transmission, similar to ensuring mail delivery with a second trip.
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP): In User Datagram Protocol (UDP), lost packets aren’t automatically resent like in TCP. UDP adopts a more relaxed approach, suitable for real-time streaming apps tolerating some packet loss. If an app requires packet retransmission, it’s up to the application to handle it, or consider switching to TCP/IP.
How to Fix Packet Loss— 6 Step-by-Step Guideline
Now you know what packet loss is as well as its causes and impacts on network performance. And believe me, this is important to fix a packet loss issue.
Follow this 6-step comprehensive guideline to fix packet loss stemming from any cause:
Step 1: Check Your Network Thoroughly and Detect Packet Loss

When you experience data lag or slow network performance, the first thing to do is- check and detect if it’s because of packet loss. Analyze network devices for failures or misconfigurations. Identify packet loss patterns to isolate root causes effectively. Employ deep packet inspection for thorough traffic analysis and security.
Regular monitoring is also a good practice to maintain good network health. Acceptable packet loss rates vary by network type and application; LANs tolerate less than 1%, while WANs accept up to 3%. Real-time applications can tolerate occasional loss, but rates above 5% significantly impact performance.
Step 2: Understand the Causes
We’ve already thoroughly explained the various causes of network packet loss. To effectively detect and resolve packet loss problems, it’s crucial to grasp these factors. Familiarize yourself with each point to enhance your ability to identify packet loss instances. This understanding empowers you to address network issues autonomously, leading to effective solutions.
Step 3: Do a Ping Test to Measure Packet Loss
Ping measures latency. Do a ping test to check your internet health and packet delivery time. Assessing connection performance involves examining upload speed and download speed. You also need to know the tolerated level of packet loss.
- Upload Speed:
This measures how quickly you can send data packets to others. Whether sharing large files via email or engaging in video calls, upload speed, in Mbps, is crucial for efficient data transmission.
- Download Speed:
It indicates how fast you can receive data packets from the server. Usually faster than upload speeds, this parameter, measured in Mbps, affects accessing online content.
- Ping:
Ping is the round-trip travel time of a data packet, reflecting connection responsiveness in milliseconds (ms). Critical for real-time applications, lower ping values indicate a more responsive connection.
- Ideal Ping and Packet Loss:
An ideal ping is below 15 ms, ensuring responsiveness. However, a ping exceeding 300 ms can cause noticeable lag. Despite a good ping, packet loss issues can persist, affecting data accuracy even with rapid delivery.
Step 4: Identify the Source of the Packet Loss
Packet loss can have different causes and you have to find out the exact source of it in your network. Deep packet inspection is a good way to do that. DPI locates, identifies, classifies, reroutes, or blocks packets with specific data or payloads. It can help you find out how to stop packet loss.
Step 5: Find Out How to Fix Packet Loss Issues
When you find the source of the problem you can find a solution for it as well. Pointing out a single solution to packet loss is difficult as it depends on the specific causes in your system. Follow the instructions below and you should be able to deal with any sort of packet loss issue yourself:
- Restart your system: If you face data lag, reboot your router and other devices first. It will resolve temporary glitches or software issues that may cause packet loss.
- Examine hardware and physical connections: Check hardware devices and all physical connections to identify if the packet loss is due to a faulty cable connection or hardware failure.
- Check for software updates: Update if you find any outdated software that may cause the packet loss. It’s better to update all necessary software regularly
- Use a wired connection: In case you are using WiFi, try a wired connection and it may help. Wired connections are more stable and less likely to have data lost in the transmission.
- Upgrade faulty hardware: Outdated hardware is a major reason behind data packet loss. Upgrade your outdated hardware if you detect it’s causing the trouble
- Optimize your network settings: Improper network configuration may cause packet loss in your network, so optimize your network settings for better performance
Step 6: Talk to an Expert If Needed

If you can’t find out the issue and resolve it yourself, contact your ISP. They will try from their end and come up with a possible solution. Or talk to a network expert if possible. Networking sometimes may seem a bit difficult to understand, so it’s quite normal if you need expert help to fix packet loss.
How to Stop/Prevent Data Packet Loss?
Prevention is always better than cure, right? Packet loss can stem from various reasons, such as network congestion, hardware glitches, or security breaches. In digital connectivity, where smooth data transmission is imperative, packet loss presents a significant hurdle.
Yet, by understanding the causes and deploying proactive measures, organizations can prevent or reduce packet loss impacts on their networks. Adhere to these vital techniques and best practices to avoid packet loss issues and uphold optimal network performance:
- Regularly monitor network performance with specialized tools
- Inspect physical network connections for any damage
- Audit network configurations to prevent loops and bottlenecks
- Prioritize wired connections over wireless ones
- Uphold robust security with antivirus and antimalware programs
Conclusion
We’ve tried here to provide a comprehensive guideline on how to fix packet loss, empowering readers to detect and address network issues effectively. While some packet loss may persist despite our best efforts, proactive prevention strategies significantly bolster network resilience. Depending on the severity of the issue and network complexity, seeking assistance from ISPs or network professionals may be necessary for critical cases.
Remember, regular monitoring and proactive maintenance are key to minimizing disruptions caused by packet loss. As the digital landscape evolves, prioritizing optimal network performance ensures seamless communication and enhances user experience, especially in the era of hybrid work environments. With vigilance and strategic interventions, organizations can reduce the impact of packet loss and foster efficient network operations.