If you are asked, “What is the most modern replacement for traditional phone systems?” Your answer would be VoIP or Voice over Internet Protocol technology, which is expected to reach $108.5 billion by 2032. Despite being a widely used technology, many of us are unaware that the quality of VoIP calls is significantly impacted by network conditions. This is where VoIP QoS emerges as a crucial component. By prioritizing voice traffic over data, VoIP QoS ensures clear and uninterrupted calls.
Often it is seen that no matter how good a company’s internet connection is, they still face call quality issues with their hosted VoIP phone services. Some of the most common problems include unclear sound, delay in audio, unexpected interruptions, and jitter. These issues can not only frustrate users but also lead to lost business opportunities, ultimately hampering the growth. If you too are experiencing these issues with your VoIP calls, then it might be the right time to get it checked.
Through this blog, we will be exploring the various aspects associated with VoIP QoS. We will understand how VoIP quality of service, when done right, can enhance the quality of your VoIP calls. We’ll cover the working of QoS for VoIP, its importance, setup procedure, and VoIP QoS best practices.
I’m sure you are ready to learn about VoIP QoS in more detail. Let’s get started!
What is VoIP QoS?
VoIP QoS, or VoIP Quality of Service, is a method that prioritizes VoIP traffic over other network data, which typically passes through a router. By default, routers prioritize traffic using the First in, First out algorithm. However, this strategy can often lead to network congestion and delays when bandwidth usage is high.
VoIP technology relies on data packets for the transmission of voice calls over the internet. For clear audio during a call, it’s crucial that these packets reach their destination in the correct sequence and within a specific timeframe. However, if these packets are lost, delayed, or delivered out of order, i.e., violating the First in, First out (FIFO) order, then this leads to issues in the voice calls. Some of the most common VoIP issues are echo, latency, packet loss and dropped calls.
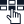
Putting QoS in place helps in ensuring that voice calls have the necessary bandwidth and resources to deliver clear, uninterrupted, high-quality audio. In simple words, it is like giving your VoIP calls a quality boost as they pass through the internet, making sure that they reach their destination without any glitch and on-time. Network administrators make use of QoS techniques to troubleshoot these issues and deliver high-quality voice calls.
Importance of VoIP Quality of Service
A lot of digital activities happen in modern-day businesses, right? Imagine it’s your office where multiple employees rely on a shared internet connection, both for personal and work-related usage. This means that simultaneously multiple devices use the internet bandwidth for online activities.
Such heavy usage of the internet often creates congestion, thus overwhelming the network. Now, if under such conditions, you try to initiate a VoIP call without QoS, then the VoIP data packets are treated no differently than other traffic. Often, this results in call quality issues like delays, interruptions, echo, and poor audio. To put it simply, without QoS, voice calls are devoid of clear communication.
It is quite frustrating when you can’t understand what the person on the other end of the call is saying. No matter if it is a critical business deal or you’re just catching up with a friend, it becomes difficult to focus when call audio is poor. In the case of businesses, such issues can have serious consequences.

Imagine trying to provide support to a premium customer when the conversation is constantly interrupted by echoes, jitter, and drops in audio. There are several other scenarios where having a high-quality call is an absolute essential, including:
- Product demonstrations and workshops
- Team meetings and discussions
- Recruitment interviews and performance reviews
With more people working from home than ever, their networks are often loaded with things like video streaming and file downloading. This can make it hard for business calls to get the needed bandwidth and priority, leading to unclear sounds. This is another reason why it’s really important to make sure that VoIP traffic receives the needed priority.
Ultimately, the importance of VoIP QoS lies in the fact that VoIP calls are highly sensitive to network conditions. Even a slight delay in packet delivery or packet loss can significantly disrupt call quality.
How does VoIP QoS Work?
The Quality of Service in VoIP works by assigning priority at different levels to different types of network traffic. Amongst the various types of data on a network, VoIP calls are typically given more preference as compared to other traffic such as emails and web browsing.
The QoS feature in VoIP makes use of several techniques to manage traffic. Let’s take a look:
-
CoS

CoS, or Class of Service, is a traffic prioritization technique in which each data packet is assigned a priority label (ranging from 0 to 7, lowest to highest respectively) to determine its importance within the network. CoS technique is primarily used in LAN environments and operates at Layer 2 i.e. data link layer. Since VoIP traffic is sensitive to latency and jitter, it is typically assigned a high CoS value.
-
DiffServ
DiffServ, or Differentiated Services, works by dividing traffic into different classes based on their requirements. It’s a layer 3 QoS mechanism that makes use of DSCP i.e. Differentiated Services Code Point in IP packets for classification and prioritization.

Traffic is divided into classes and assigned a DSCP value to each IP packet, which determines their priority level. Typically, VoIP packets are marked with a higher DSCP value ensuring expedited transmission, lower latency and minimal packet loss.
-
PBR

PBR, or Policy Based Routing, is a layer 3 technique using which administrators can route traffic based on some predefined criteria, rather than just the IP address. Through PBR, VoIP traffic can be routed via some specific low-latency paths, bypassing the standard routing, further optimizing call clarity and reliability.
Now let’s imagine a scenario. You are a business with a stable internet connection. Every time an email arrives, a call is made, or a website is browsed, data moves from one end to the other. When data travels, the QoS comes into action and sorts it into different categories or classes, and ensures that priority is given to time-sensitive data such as video calls. So even when internet usage is at its peak, QoS will ensure that your calls go clear and uninterrupted.
6 Key Components of VoIP QoS
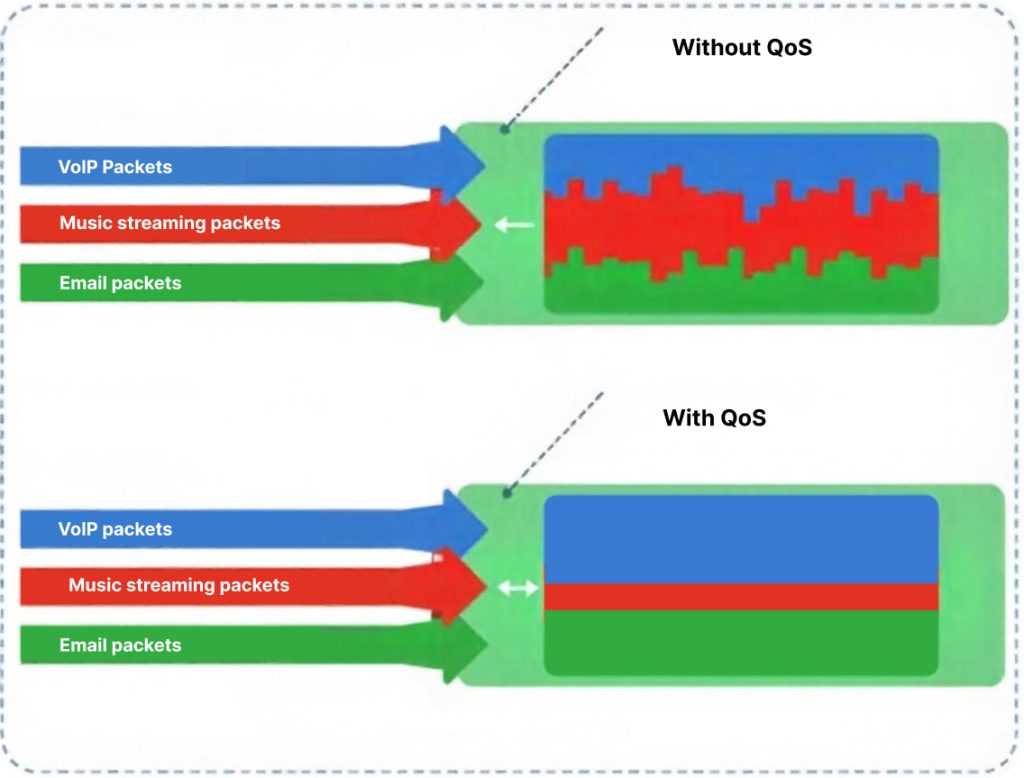
VoIP QoS consists of 6 key components, which are explained as below:
Bandwidth Allocation
It is the maximum amount of data that can be transmitted over a network connection within a specific time frame. In the case of VoIP calls, sufficient allocation of bandwidth indicates that calls can happen smoothly; otherwise, users may experience choppy or distorted audio.
Insight – VoIP calls typically require 100 Kbps per line.
The bandwidth allocation component of QoS ensures that there is enough data capacity to handle voice calls smoothly. So even in times of high network traffic, reliable voice communication is ensured.
Latency Management
It is the time a data packet takes to travel from its source to the destination. So, a low-value latency is typically essential for real-time communication. In case the latency value goes high, users may experience delays in conversation, such as echo or noticeable delays between speaking and hearing a response.
Insight – The acceptable latency for VoIP calls should be under 150 milliseconds for good quality.
Latency is an inherent aspect of VoIP, but excessive delays can severely affect call quality. Voice data packets are particularly vulnerable when delays exceed 150 milliseconds in either direction.
The latency management component of the QoS tackles the problem of delays in conversations. By minimizing lags in voice communication, it improves the overall calling experience for users.
Jitter Control
Jitter refers to variations in the delay between data packets. In simple terms, it is the inconsistency in packet delays that disrupts the smooth flow of audio.
Insight – Jitter needs to be kept below 30 milliseconds for optimal call quality.
When network jitter surpasses 30 milliseconds, it can dramatically impact voice calls, resulting in a noticeable decline in audio quality. By managing the variation in data arrival times, the jitter control component of QoS ensures consistent and high-quality audio transmission.
Packet Loss Prevention
Packet loss happens when data packets are lost or corrupted during transmission. Voice data packets are particularly sensitive to this issue.
Insight – Packet loss levels of 1% or less are considered acceptable.
When the packet loss rate exceeds 3%, it can lead to a significant deterioration in call quality, making it difficult to understand the conversation. This can result in dropped calls, missing audio clips, and even distorted sound.
The packet loss prevention component of QoS addresses the problem of interruptions during conversations and ensures reliable voice transmission without loss of data.
Traffic Prioritization
Priority refers to the preference assigned to different types of network traffic. As explained earlier in this post, VoIP QoS often leverages DiffServ (Differentiated Services) marking for traffic prioritization.
Usually, VoIP traffic is given higher priority compared to other types of traffic. So, basically, the traffic prioritization component of QoS ensures that VoIP calls are delivered smoothly, even during periods of high network congestion.
Buffering
Buffering is the process of temporary storing of data to compensate for variations in delay. In the case of VoIP, this method helps smooth out jitter and enhance the overall call quality. For situations where there’s a sudden spike in traffic, data packets can be held in a buffer until the network can handle them. This results in a consistent flow of data.
VoIP QoS Pros and Cons
We have learned that QoS addresses several call quality issues in VoIP calls; however, we must look at the other side of the coin as well. Let’s explore the pros and cons of QoS in VoIP to better understand its usefulness.
| Pros | Cons |
| Improved call quality (reduced latency, jitter, and packet loss) | Increased network complexity (configuration challenges, potential for misconfiguration) |
| Increased network efficiency (prioritization of voice traffic, optimized bandwidth usage) | Higher Costs (specialized equipment, technical support) |
| Enhanced user experience (higher satisfaction, increased productivity) | Limited scalability (dynamic network conditions, difficulty handling large-scale networks) |
Best Practices to Optimize Your VoIP QoS
To optimize your VoIP QoS, you need to learn and implement various practices that keep your voice traffic at priority, ensuring clear, uninterrupted and consistent communication.
First of all, understand that two core components of VoIP are : the router and the network setup, both of which are unique. It’s always a good idea to check the instructions provided by your internet vendor or network equipment provider. They often have specific guidelines on how to prioritize voice traffic.
To make the job easy for you, here’s a list with detailed explanations about the 10 best practices:

Keep Voice Traffic at Highest Priority
The top rule to ensure that voice packets are delivered first, even in a congested network, is to set the highest priority to voice traffic. But how do you do that practically? The answer is: set your voice calls to DSCP 46. With the aim to treat voice calls with highest priority, you can find the option to set RTP packets to DSCP 46 in the QoS section of your router settings. We have already learnt that DSCP is a special code that tells your router to prioritize voice calls over other traffic. Make sure you set this for both incoming and outgoing calls.
Prefer Creating a Dedicated VoIP Network
It is a good practice to create a separate network for VoIP traffic. While this isolates voice traffic from other traffic on the network, it eliminates the chances of interference and thus improves call quality.
Enable Trust Mode with Strict Priority
Advanced routers and network switches come with “Trust Mode” and “Strict Priority” options. You need to enable these options to set priority for voice calls over other traffic.
Ensure Adequate Bandwidth
To ensure high call quality, you need to ensure sufficient bandwidth for VoIP traffic. Lower bandwidth levels can overload the network, resulting in call quality issues like jitter and packet loss. It is best if you can estimate the required bandwidth based on the number of simultaneous calls and the desired quality of service.
Use Low-Latency Routers
Implementing high-latency routers to route your VoIP traffic can lead to delays in packet delivery that affect the voice quality. Therefore, it is good to opt for routers with low-latency processing capabilities, such as routers with hardware acceleration for VoIP traffic.
Enable Jitter Buffering
To smooth out variations in data packet arrival times, you simply need to enable the jitter buffering option on VoIP endpoints. This can be done by configuring jitter buffers on IP phones and softphones to an appropriate level.
Regularly Monitor Your Network
For optimal network performance, you need to keep an eye on your network on a regular basis. This way, you can identify any potential issues before they impact the quality of voice calls. Network monitoring tools, which are readily available online, are particularly helpful for tracking issues like packet loss, jitter, and latency.
Protect Your Network
Security breaches can also disrupt voice communication, which is why you need to secure your network from attacks and unauthorized access. Some effective security measures to be taken are installing firewalls, implementing intrusion detection systems, and using strong authentication methods.
Use Power Over Ethernet (PoE)
Another effective approach to improve voice communication is reducing the number of cables and potential points of failure. You can do this by using PoE to power your VoIP phones and other network devices.
Update Your Firmware Regularly
It is important to keep your VoIP devices and network equipment up-to-date. You can do this by creating a maintenance schedule for firmware updates, which often includes bug fixes and performance enhancements.
Final Recommendations
Statistics reveal that “more (36%) software buyers go with VoIP than any other type of voice service.” highlighting the importance of implementing VoIP QoS for ensuring crystal-clear and uninterrupted voice communication.
By prioritizing voice traffic and optimizing network resources, businesses can significantly enhance call quality, boost employee productivity, and elevate overall customer satisfaction.
While setting up VoIP QoS, you may encounter several unfamiliar aspects and require technical expertise or assistance. However, remember that the long-term benefits, in terms of improved communication and reduced network congestion, far outweigh the initial investment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common issues with VoIP calls?
Common VoIP call issues include poor call quality, dropped calls, jitter, echo, packet loss and excessive latency.
How can QoS settings improve VoIP performance?
QoS settings prioritize VoIP traffic over other types of data. It ensures consistent performance, reduced latency, and improved voice quality.
Does QoS slow down the Internet?
Not necessarily, but it may happen in some situations. QoS manages bandwidth by prioritizing time-sensitive traffic, such as video calls, over less time-sensitive traffic, such as downloads. During peak network usage or high network congestion, QoS may reduce bandwidth for low-priority activities to maintain optimal performance for high priority applications.
How can I configure QoS for VoIP on a router?
Access your router’s QoS settings through the management interface, then prioritize VoIP traffic by setting rules based on IP addresses, ports, or protocols. It is best to get in touch with your internet service provider and VoIP service provider as they can guide you with the exact steps to configure VoIP QoS on your router.
How can I troubleshoot VoIP QoS problems?
You may consider checking network connectivity, verifying QoS settings, updating firmware, and consulting with your network provider for assistance.
Which type of traffic is essentially managed through QoS?
Real-time voice communication, video traffic, online gaming and time-sensitive communications are some different types of network traffic that typically need prioritization with QoS settings.
What is the ideal bandwidth for VoIP calls?
For high-quality audio calls, it’s recommended to have a stable internet connection with a bandwidth speed of at least 100 kbps per call.
How can VoIP QoS be monitored?
VoIP QoS can be monitored using various tools and techniques, such as network analyzers, packet sniffers, and performance monitoring software.