A recent survey conducted by JP Morgan shows that 94% of companies had taken serious steps to harden VoIP security. Why? Because they think VoIP threats and vulnerabilities like payment fraud, malware, service theft, and spoofing have been increasing significantly.
Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) has revolutionized business communication, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Yet, with its rise in popularity, concerns over VoIP security have also escalated. IT leaders frequently inquire about the security of VoIP phone systems, mindful of the potential risks posed by cyber threats.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of VoIP security, addressing common concerns and providing actionable insights to mitigate risks effectively. From understanding the fundamental differences between VoIP and traditional landlines to exploring the latest security issues and encryption protocols, we will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to fortify your VoIP infrastructure.
Why VoIP Security Matters
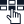
Now, you may wonder why VoIP security is so important. In the JP Morgan survey we mentioned earlier, they found that businesses face about 48% of malware attacks (including ransomware) every year. Other attacks include 23% payment fraud,13% theft of intellectual property, 9% disruption of service or company website, 3% data manipulation, and only 4% out of any concern.
Lumen Technologies found a VoIP threat spike in its 2022 Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack Quarterly Report and discovered a 315% rise compared to the first quarter of 2022. Twitter faced a comparable attack in 2020, with 45 high-profile accounts, including those of Barack Obama, Kim Kardashian, and Bill Gates, exploited to promote a cryptocurrency scam, resulting in significant financial losses.
VoIP security is critical for businesses of all sizes. Despite its cost savings and functionality, VoIP is a prime target for attackers. Unique risks like call interception and caller ID spoofing underscore the need for robust security measures. High-profile breaches, like Twitter’s, highlight the real-world impact of VoIP vulnerabilities.
The lack of regulatory protections leaves customers financially liable for fraud. Choosing a trusted provider and educating employees are vital steps in safeguarding against attacks. VoIP security isn’t just about compliance—it’s essential for business resilience in today’s interconnected world.
What is Encrypted VoIP?
Encrypted VoIP refers to the practice of securing voice data transmitted over the internet by converting it into an unreadable format through encryption algorithms. This process ensures that even if intercepted, the data remains incomprehensible to unauthorized parties.
There are two main types of encryption employed in VoIP:
- Signalling Encryption: This type safeguards the data responsible for establishing and managing VoIP calls, encompassing details like call initiation and termination. Encryption protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) are typically utilized to secure this signaling data.
- Media Encryption: Media encryption protects the voice data transmitted during calls. Voice data is encrypted using protocols like Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) or Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS). This ensures that intercepted voice packets remain incomprehensible without the decryption key.
How VoIP Encryption Works

To understand how VoIP Encryption works we have to deep dive into the transmission process:
Data Transmission and SRTP
Voice data packets are secured using the Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) or Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) applying the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for encryption and message authentication, providing defense against breaches and cyber threats.
Additionally, Transport Layer Security (TLS) or SIP over TLS encrypts and safeguards call details like caller information, preventing tampering and eavesdropping. Quality VoIP providers ensure the availability of both TLS and AES Encryption for enhanced security.
What is End-To-End Encryption?
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) is a cybersecurity measure that directly encrypts communication data between endpoints, ensuring that third parties cannot access call or message data as it travels between sender and recipient.
Unlike standard TLS encryption, which only encrypts client-to-server communication, E2EE safeguards against various threats such as eavesdropping, data manipulation, and unauthorized access by utilizing encryption and decryption keys to protect data both in transit and at rest. It’s essential to verify that end-to-end encryption is enabled before utilizing your VoIP system, as it may only sometimes be the default setting.
Traditional Phone Systems vs. VoIP
Traditional phone systems, operating over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), have been a staple for communication for over a century. However, they rely on analog technology and physical wiring, making them vulnerable to interception and attacks, particularly through practices like phreaking. Despite attempts to secure the PSTN, vulnerabilities persist, especially within Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems.
On the contrary, VoIP offers a more secure alternative, leveraging encryption and authentication protocols to protect communication data transmitted over the internet. VoIP systems operate over data networks, eliminating the need for physical wiring and offering enhanced security features that traditional landline phones lack.
VoIP systems are cost-effective, as they eliminate the need for telephone wiring and allow for easy scalability without additional infrastructure costs. Users can also enjoy flexibility, working from anywhere with internet access, thanks to virtual phone identities and SIP calling apps.
While VoIP may have advantages in security and cost-efficiency, traditional landline phones still hold sway in terms of reliability, especially in areas with poor internet connectivity or during power outages. They offer a fallback option in situations where internet-based communication is compromised.
VoIP phone services provide the following security advantages compared to traditional phone systems:
- VoIP calling apps provide real-time monitoring of calling plan usage
- Stringent enforcement of toll-free calls
- Advanced encryption technology to prevent eavesdropping attempts
- Robust voicemail features with email delivery integration
Common VoIP Security Risks and How to Prevent Them
VoIP security is a major concern now for businesses, but don’t worry, we will discuss all possible solutions here. Although it’s difficult to prevent 100% security and privacy attacks, adopting a proactive stance towards VoIP security significantly diminishes both their frequency and the extent of their consequences.
Packet Sniffing
Packet sniffing represents a prevalent VoIP software attack, wherein hackers disrupt the transit of voice data packets to pilfer and record unencrypted information. By hijacking your router, packet sniffers manipulate data streams through a black hole attack, leading to either degraded network performance or a total loss of network connectivity. This enables packet sniffers to illicitly obtain usernames, passwords, and other confidential data.
How to Prevent Packet Sniffing
- Use a reliable VPN
- Turn on end-to-end encryption (E2EE)
- Enable network monitoring with real-time alerts
- Avoid using public Wi-Fi
DDoS Attack
A DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attack is a malicious act orchestrated by a network of hacker-controlled botnets with the aim of overwhelming networks, websites, and servers, thereby disrupting access to VoIP services for businesses.
These attacks are characterized by abnormal and prolonged bandwidth spikes, 503 HTTP Error Responses, slowed service, and sudden surges in traffic from similar devices, IP addresses, or locations. DDoS attacks effectively prevent organizations from accessing their VoIP services, leading to significant disruptions in communication and business operations.
How to Prevent DDoS Attack
- Use a dedicated and reliable VoIP Internet connection for VoIP traffic
- Use managed encryption
Ransomware & Malware
Computer viruses, ransomware, and malware pose a significant threat to VoIP systems, leading to various security issues and disruptions in communication. These malicious programs consume network bandwidth, contributing to signal congestion and call breakdowns. Additionally, malware corrupts data being transmitted across networks, resulting in packet loss during VoIP calls.
Furthermore, malware creates Trojan backdoors within data networks, leaving businesses vulnerable to future cyber attacks. These backdoors serve as entry points for hackers to tamper with calls or steal sensitive information relayed through VoIP systems.
How to Prevent Malware
- Enable E2EE encryption
- Check for network infection regularly
- Be aware of dangerous sites and purchase routes that actively block malware
- Strengthen security with anti-viruses and VoIP-compatible firewalls
- Always use strong passwords
Vishing
During vishing attacks, hackers use VoIP to impersonate trusted entities over phone calls, aiming to deceive businesses into divulging sensitive information like passwords and credit card numbers. Caller ID spoofing is employed to lend legitimacy, presenting false information such as the caller appearing to be from the victim’s bank. This tactic induces urgency or fear, coercing victims into sharing confidential data. Unlike email phishing, vishing exploits VoIP systems by manipulating caller IDs, posing substantial security risks to businesses dependent on phone communications.
How to Prevent Vishing
- Avoid providing personal information over the phone to anyone
- Verify phone requests, even if they seem familiar
- You may join the Do Not Call Registry to manage inbound calls
- Initiate Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) wherever possible
- Train agents properly to avoid giving any sensitive information to fraud calls
SPIT
SPIT, an acronym for Spam over IP Telephony, mirrors the tactics of phishing attempts and email spam but targets VoIP phone numbers. This form of spam inundates VoIP systems with prerecorded messages, aiming to disrupt service availability by overwhelming phone numbers. Additionally, SPIT messages frequently contain malicious software or viruses, posing a dual threat of service denial and potential security breaches.
How to Prevent SPIT
- Use effective firewalls to identify and control Spam
- Dialpads often offer call-blocking and spam-prevention features. Use these features
- Use reputed and reliable VoIP service only
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
In a man-in-the-middle attack targeting VoIP calls, hackers position themselves between the network and the intended recipient. Typically exploiting public or unsecured WiFi networks, they reroute calls through their servers, facilitating the injection of malware, viruses, or spyware into intercepted calls.
How to Prevent Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
- Avoid public Wi-Fi
- Use a VPN
- Enable WAP/WEP encryption at access points
- Maintain router login credential
Toll Fraud
Hackers exploit business phone systems to generate a high volume of international calls, aiming to profit from the revenue generated. This scheme, known as toll fraud or International Revenue Sharing Fraud (IRSF), involves the misuse of Premium Rate Numbers (PRNs). It poses challenges for detection and prevention due to its reliance on complex networks of mobile systems and multiple operators.
How to Prevent Toll Fraud
- Activate 2FA (two-factor authentication)
- Use script breaker like Captcha
- Set rate limits on call duration and restrict geo-permissions
Call Tampering
The next VoIP security threat on our list is call tampering. Call tampering involves cybercriminals disrupting business phone calls by inserting noise packets into the call streams. This action diminishes call quality and can lead to both parties terminating the call prematurely. Additionally, hackers may obstruct the transfer of packets to their intended destination, resulting in unreliable and distorted service characterized by intermittent reception and extended periods of silence.
How to Prevent Call Tampering
- Enable E2EE (end-to-end encryption)
- Make sure your VoIP service has TLS encryption to authenticate data packets
- Endpoint detection software can also help
VOMIT
Voice over Misconfigured Internet Telephones, commonly known as VOMIT, represents a VoIP hacking tool used to convert conversations into files that can be played anywhere. This method facilitates the extraction of sensitive information from business phone systems. By intercepting these converted files, attackers can gather various types of data, including call origins, usernames, passwords, phone numbers, and bank information.
How to Prevent VOMIT
- Choose a cloud-based VoIP provider that encrypts calls before they are initiated
- Work with HIPPA & HITECH compliant providers
- Prefer a private PBX network rather than a public one
Best Practices to Secure Your VoIP System
Now you know almost all types of VoIP security risks a business may face and we have also covered some points on how to prevent these threats. Below here we’ve summarized some VoIP security best practices that are crucial to mitigate VoIP security issues.
- Strong Password Policies
Implement strong password policies to prevent brute force attacks and ensure employees use unique passwords regularly. Policies should prohibit the use of easily guessable passwords and require regular password updates.
- Avoid Public WiFi Networks
Instruct employees to avoid using public WiFi networks for VoIP access to mitigate the risk of malware and viruses spreading. Public networks are often unsecured and can expose the VoIP system to potential security threats.
- Routine Security Audits
Conduct routine security audits performed by independent agencies to assess and patch vulnerabilities in the system. Audits should include patching procedures, gateway assessments, firewall configurations, and cyberattack simulations.
- Consistent Software Updates
Consistently update VoIP software to access security patches and prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities. Automatic updates should be enabled to ensure the system is protected against emerging threats.
- Protection of BYOD/Mobile Devices
Protect BYOD/mobile devices by enabling end-to-end encryption and using session border controllers for remote connectivity. This ensures that communications remain secure even when accessed from personal devices.
- Audio Fencing
Utilize audio fencing to eliminate background noise and enhance call privacy. This feature creates a virtual “fence” environment, ensuring that calls cannot be overheard and sensitive information remains confidential.
- Spam Call Blocking
Features like spam call-blocking provided by trusted VoIP providers minimize the risk of malicious calls. Automatic spam blocking systems and user-level settings can control how calls are handled, reducing the likelihood of security threats.
- Deletion of Inactive Accounts
Promptly delete inactive employee accounts to prevent unauthorized access to the system. Removing inactive accounts reduces the risk of security breaches and ensures that only authorized personnel have access to the VoIP system.
Features to Look for in a Secure VoIP Service Provider
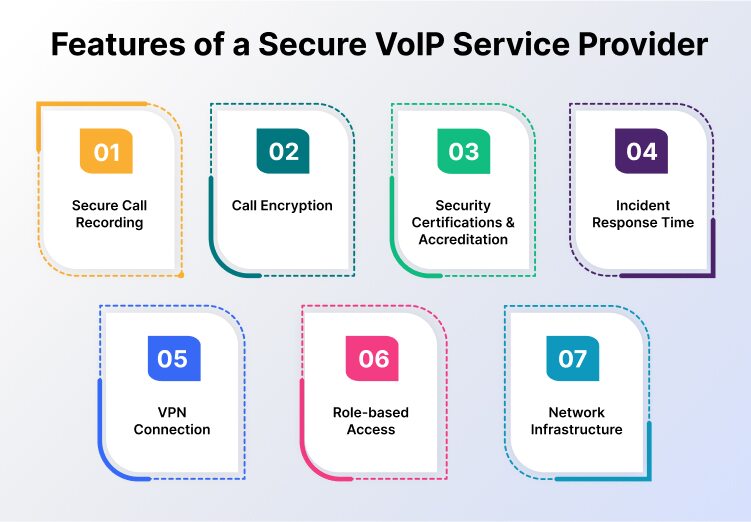
When choosing a VoIP provider for your business, check if they have the following features in their service:
1. Secure Call Recording
Ensure that the VoIP provider offers secure call recording features, including encryption of recorded data at rest and in transit. Look for options to customize call recording settings to comply with legal requirements and protect sensitive information.
2. Call Encryption
Encrypted VoIP providers implement robust encryption protocols such as TLS (Transport Layer Security) and SRTP (Secure Real-time Transport Protocol) to protect voice traffic from interception and eavesdropping.
3. Security Certifications & Accreditation
Verify that the VoIP provider holds relevant security certifications and compliance accreditations such as SOC 2 Type 2, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and ISO/IEC 27001. These certifications ensure that the provider adheres to industry best practices and meets stringent security standards.
4. Incident Response Time
Inquire about the provider’s incident response time and protocols for handling security incidents. Look for quick and efficient responses to security threats, including notification procedures and service restoration timelines.
5. VPN Connection
Check if the VoIP provider offers VPN (Virtual Private Network) connections to encrypt voice traffic and ensure secure communication, especially for remote teams accessing the VoIP system from unsecured networks.
6. Role-based Access
Choose a provider that offers role-based access controls to manage user permissions and restrict access to sensitive features and data. Ensure that the provider supports authentication mechanisms such as single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) for enhanced security.
7. Network Infrastructure
Evaluate the provider’s network infrastructure, including data centers and server redundancy. Look for multiple data centers in geographically diverse locations to ensure service continuity and resilience against network disruptions.
By prioritizing these features when selecting a VoIP service provider, businesses can enhance the security of their communications and safeguard sensitive information effectively.
Conclusion
For modern businesses, safeguarding VoIP security is paramount. It’s the shield that protects vital communication channels from cyber threats. Although it’s difficult to ensure a 100% secure VoIP system, by implementing robust encryption and staying vigilant, businesses can maintain seamless communication experiences while fortifying their defenses against potential breaches. So, prioritize VoIP security today to safeguard your organization’s valuable information against any potential cyber threat.