When designing a networking system, the most important thing you’ll need is a network switch. But how do you choose a network switch that meets your specific requirements? Managed vs unmanaged switch, which one do you prefer? Your answer probably will be, It depends. That’s right, the choice of network switches depends on specific needs and requirements.
If you have skilled administrators or engineers and you want a more manageable, controllable system, managed switches are your best pick. On the other hand, unmanaged switches are plug-and-play, inexpensive devices for smaller businesses or personal use.
Before discussing the difference between managed and unmanaged switches, let’s talk about how a network switch works.
How Does a Network Switch Work?

A network switch is also called a switching hub or bridging hub. It’s a networking hardware that connects all devices on a LAN (Local Area Network) using packet switching. The primary role of a network switch is receiving and forwarding data among devices within the network.
Alright, let’s break down how a network switch works in simple ways—
In a network, switches act as connection points for devices. They’re commonly used at the edge of a network, where your computers, printers, and other gadgets connect. But they’re not just limited to it; they can also be used deeper within the network to link different switches.
These switches can handle various types of networks like Ethernet, Fibre Channel, RapidIO, and more. They work at different layers, with layer 2 managing bandwidth within one technology. However, when you need to link different technologies like Ethernet and Token Ring, you might want to involve layer 3 or routing. Routers are like traffic cops, ensuring smooth communication between different technologies.
Switches can also create a mirror image of data through port mirroring, sending it to external devices like intrusion detection systems. This helps keep an eye on what’s happening in the network.
In modern setups, some switches support Power over Ethernet (PoE). This nifty feature lets devices like VoIP phones or wireless access points draw power directly from the switch, eliminating the need for a separate power supply.
What is a Managed Switch?

Managed switches are like the smart brains of a network, offering advanced features that need some tech knowledge. Unlike a basic unmanaged switch, managed switches let you customize each port, acting like personal control panels for network connections.
A key feature is the ability to set up ports as trunks, creating data superhighways for efficient traffic flow between switches or servers needing access to multiple VLANs. Control is a big deal with managed switches, allowing you to decide who accesses data and how it moves through the network, acting like gatekeepers for digital security.
They often support Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), providing real-time updates for troubleshooting and insights into network stats, helping admins make informed decisions over time. Ideal for larger networks where security is crucial, a managed switch handles heavy workloads at the core layer of data centers, offering tools to keep everything running smoothly.
However, they aren’t for the tech-shy. A managed switch requires expertise, usually involving IT professionals for proper setup and management. In return, you get a network superhero perfect for larger organizations or those dealing with sensitive information, offering precise control and power.
What is an Unmanaged Switch?

Well, you already got it from the term ‘Unmanaged Switch’, didn’t you? These switches do not provide any configuration features and you don’t get full control over your network. They are plug-and-play devices for comparatively simpler networks. Layer 2 switching does this automatically to move packets around.
Unmanaged switches are the easygoing ones in the networking world. Think of them as the simpler connectors for your devices – plug them in, and they start working. No admin fuss, and no logs to check. Designed for simplicity, these switches are perfect for small setups.
Using auto-negotiated ports, they become universal translators, ensuring all devices communicate seamlessly in the same broadcast domain. While they may not handle complex tasks like VLANs, unmanaged switches are the silent workers, effortlessly handling basic networking.
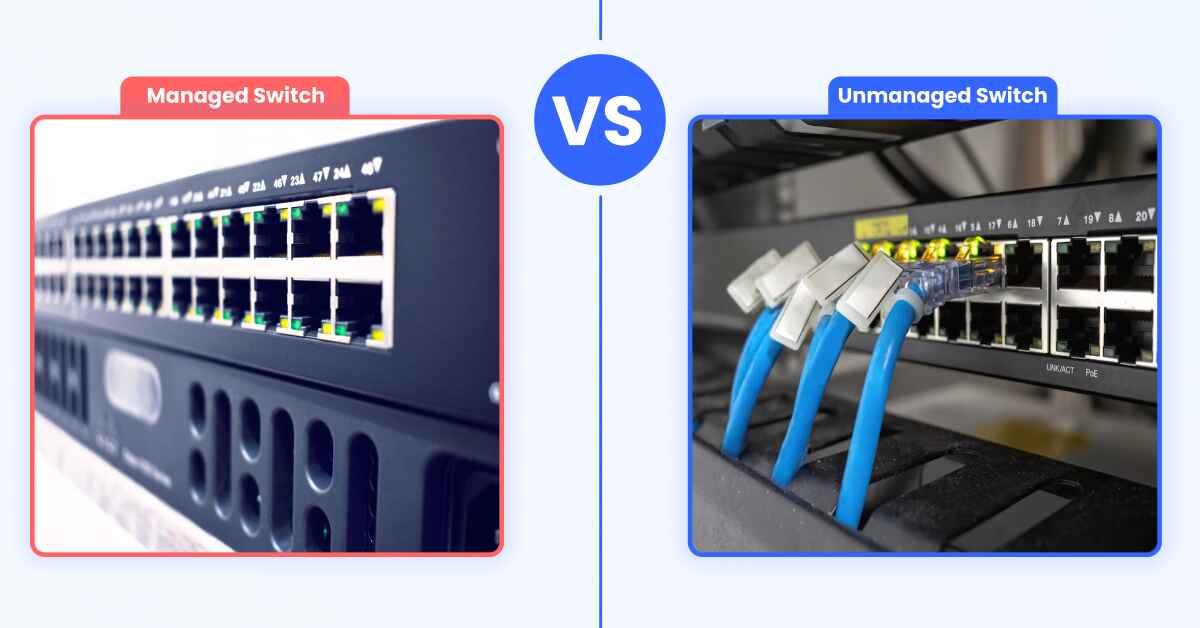
Difference Between Managed and Unmanaged Switch
What are Locally-managed vs Cloud-managed Switches?
Now, beyond the ‘managed vs unmanaged switch’ topic, let’s talk about locally managed vs cloud-managed switches.
Locally managed switches are managed and controlled locally. They need an administrator, to be right there, either hooked up directly to the corporate network or having some fancy remote access skills. It’s like having a ship captain who needs to be on the boat to make decisions – hands-on control.

On the flip side, cloud-managed switches are controlled up there in the digital clouds, and all an administrator needs is good old internet access. No need to be physically tied to the network or have superpowers for remote access. It’s like having a captain who can steer the ship from anywhere with just a Wi-Fi connection – talk about flexibility!
Think about a scenario where your network spans different locations, maybe even across continents. This is where cloud-managed switches shine. They make the remote management game a breeze. Just log in from wherever you are, and you can control it.
So, locally managed switches want you to be on the deck, either physically or virtually nearby. On the other hand, cloud-managed switches give you the freedom to captain your ship from anywhere with internet access. It’s all about choosing the style and convenience you want to experience.
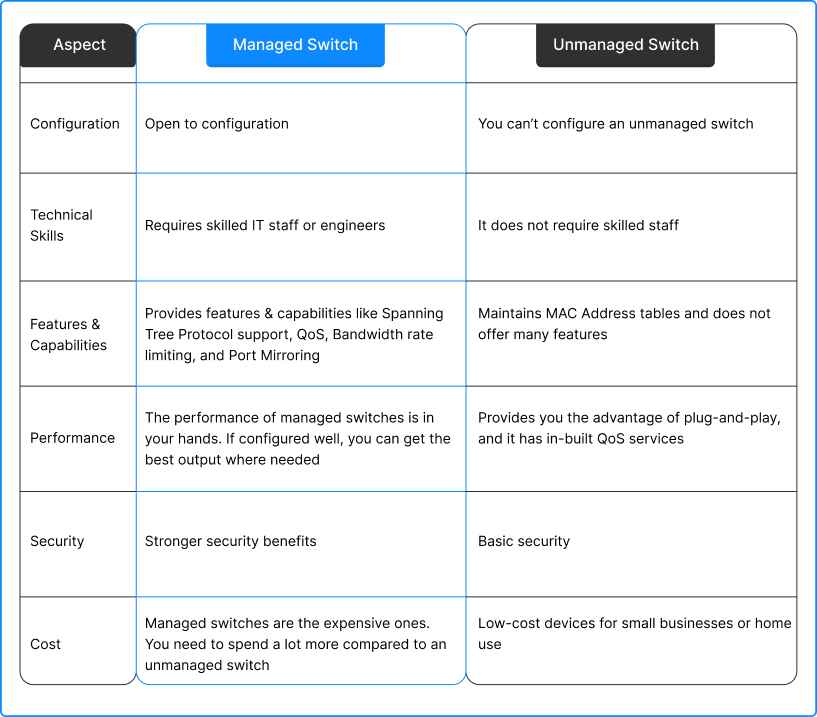
5 Characteristics of Managed Switch and Unmanaged Switch
Features and Benefits You Can Expect from a Network Switch
If you are about to set up a computer network, unmanaged switch vs managed switch, which one to get? Specifically, what features should you expect from a particular network switch? Here is a brief guide on this.
A network switch offers several features and benefits that contribute to efficient and secure data transfer. With multiple ports for connecting devices, switches facilitate fast data transmission within a local network. You can choose between managed and unmanaged options based on your specific needs, with managed switches providing extra controls like VLAN support and Quality of Service (QoS) features.
Some switches support Power over Ethernet (PoE), enabling direct power supply to devices through network cables. The benefits include improved network performance, enhanced security with access controls, scalability for easy network expansion, and flexibility in network design. Additionally, switches often come with diagnostic tools for troubleshooting, making them a cost-effective and essential component for maintaining a well-functioning network. As we are focusing on the ‘managed vs unmanaged switch’ discussion, let’s check what features and benefits each of them has.

Features of a Managed Switch
- Versatile Deployment: Managed switches support various topologies like mesh, aggregation, and Spanning Tree, providing flexibility and enhanced security options.
- Advanced Security: Delivers precise monitoring of data flow within the network, enabling quick identification and resolution of any security breaches.
- Device Optimization: Equipped with Quality-of-Service (QoS) features, most managed switches empower administrators to assess device performance and address any issues promptly.
- Efficient Network Management: Ideal for large networks, managed switches facilitate remote management, software-defined network management, and the provision of power to end-point devices, streamlining overall network operations.
Features of an Unmanaged Switch
- Plug-and-Play Ease: Unmanaged switches are effortlessly deployable, operating as a plug-and-play solution for quick setup.
- Simple Network Topologies: Suited for uncomplicated network structures like daisy chains and star configurations, making them user-friendly.
- MAC Address Storage: Unlike Ethernet hubs, unmanaged switches can store MAC addresses, enhancing efficiency in data transmission.
- Cost-Effective Choice: A budget-friendly alternative compared to managed switches, providing a cost-effective solution for basic networking needs.
Managed vs Unmanaged Switch: How to Choose?
Choosing between managed and unmanaged switches is an important decision in establishing an effective network infrastructure. A managed switch offers advanced features and customization options, making them ideal for larger networks with specific requirements.
On the other hand, an unmanaged switch is straightforward and easy to use, making it suitable for smaller setups with less complexity. Here, we’ll explore the key factors to consider when deciding between managed and unmanaged switches, helping you make an informed choice based on your network’s unique needs and your level of technical expertise.
When is a Managed Switch the Best Option?
When considering your network needs, a managed vs unmanaged switch is a usual case for all. Managed switches shine in specific scenarios, making them the best option for your network under certain circumstances.
- Enhanced Security: Managed switches can disable ports, preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding against viruses and data breaches.
- Effective Monitoring: Equipped with protocols like SNMP, managed switches allow remote monitoring of network health and the status of individual devices, ensuring proactive management.
- Traffic Prioritization: Prioritization of LAN traffic is crucial for smooth network operation. Managed switches enable this, ensuring that essential data takes precedence and heavy traffic doesn’t disrupt functionality.
- Redundancy for Reliability: A managed switch offers options like Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and ring topologies, ensuring network functionality even in the event of link or device failures.
- Segmentation for Efficiency and Security: Managed switches support Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), allowing the segmentation of network traffic. This reduces unnecessary data flow, improving system performance, and adding an extra layer of security.
Use Cases of an Unmanaged Switch
An unmanaged switch is best in scenarios where simplicity and cost-effectiveness are important. These switches are tailored for specific use cases where advanced features aren’t a top priority. Check the following cases as examples—
- Home Networks: An unmanaged switch is perfect for home networks, where ease of use and straightforward setup are key considerations. Most home setups don’t demand the advanced features that come with managed switches, making unmanaged switches an ideal and hassle-free choice.
- Small Businesses: In small business environments with limited network complexity, unmanaged switches shine. These setups typically involve a handful of devices, and the straightforward nature of unmanaged switches suits such environments perfectly. The cost-effectiveness of unmanaged switches aligns well with the budget constraints often faced by small businesses.
- Basic Connectivity Needs: Any scenario that requires basic connectivity without the need for intricate network management can benefit from unmanaged switches. This includes situations where the primary goal is to establish a reliable connection between devices without delving into complex configurations.
- Limited IT Resources: Unmanaged switches are a practical choice when IT resources are limited. In environments where there might not be dedicated IT personnel or the need for constant monitoring, the plug-and-play simplicity of unmanaged switches becomes a valuable asset.
- Cost-Conscious Deployments: Situations where budget constraints are a significant consideration make unmanaged switches a preferred choice. These switches offer a cost-effective solution for scenarios where advanced features provided by managed switches might be overkill.
Conclusion
For those who are navigating the digital world of connectivity, the difference between managed and unmanaged switches holds significant weight in the tech world. Managed switches carve a niche with advanced features, delivering unparalleled control, strong security, and optimized performance. On the other hand, unmanaged switches emerge as the pragmatic choice, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making them the go-to for streamlined connectivity.
Managed vs unmanaged switch – which one you pick, depends on your specific needs and preferences. Either way, understanding the difference between them, the features and benefits they provide, and their working process empowers you to make the right decisions.