Have you ever had a video call freeze at the most crucial moment, leaving you staring at a pixelated frozen frame while the conversation continues without you? Or perhaps you’ve experienced that frustrating lag in online gaming, where victory slips through your fingers due to delays you can’t quite put your finger on. If these scenarios sound all too familiar, you were a victim of network packet loss – the silent disruptor of your connected life. What is packet loss, then?
Imagine packet loss as the tiny ant on an elephant’s back – seemingly insignificant, yet capable of weakening your network and disrupting your digital experiences. Whether you’re an individual navigating the web or a business relying on seamless connectivity, packet loss in networking is a common issue. From video conferencing and VoIP to cloud-based applications and remote work, the efficiency of your network is important for smooth operations.
In this article, we are going to demystify the concept of packet loss and understand its impact on network efficiency. We will also cover how to detect packet loss and fix it. So, let’s understand packet loss meaning in a minute first, would we?
What is Packet Loss in Networking?
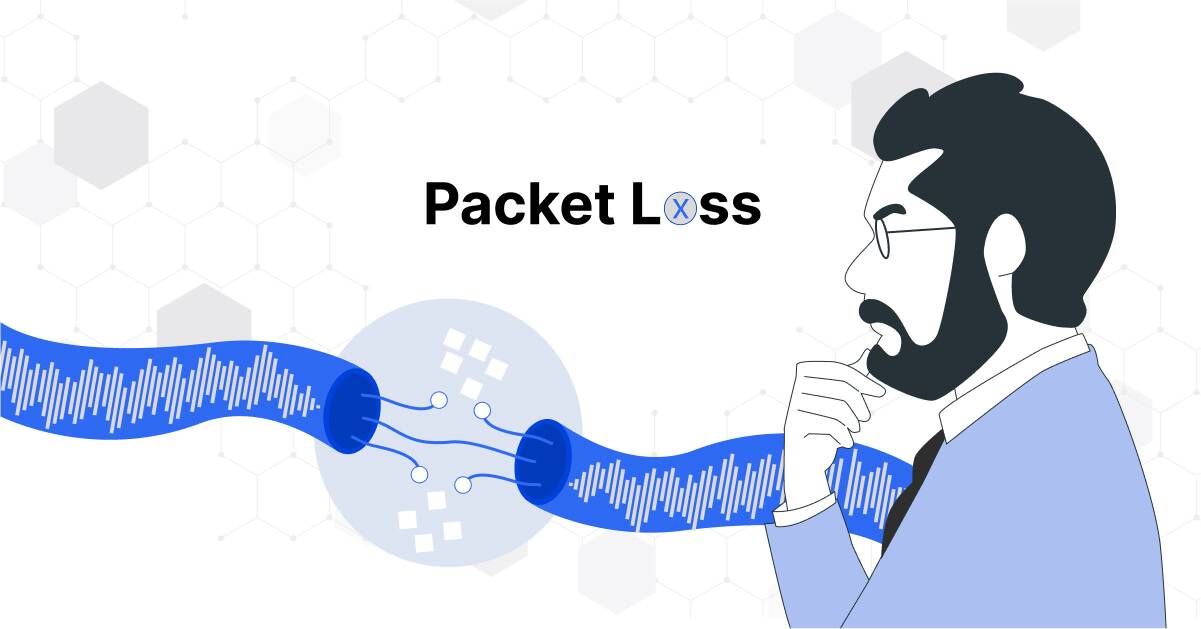
In simple terms, packet loss happens when data packets traveling through a network go missing, failing to reach their destination. It’s like sending a letter only to discover parts of it mysteriously vanished in transit, causing disruptions in everything from video calls to online gaming.
When exchanging data on any network, information travels in small units called packets. Each packet, like a numbered puzzle piece, carries a portion of the data and is directed to its destination. When one or more of these packets go astray, that’s packet loss.
Network packet loss isn’t just a random glitch; errors can trigger it during data transmission, especially in wireless networks, or when network congestion hits a peak. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), the maestro behind these packet performances, detects packet loss and it knows how to fix packet loss to ensure reliable communication.
Real-time applications like streaming media or online games bear the brunt of packet loss, affecting the user’s quality of experience. From downloading files to engaging in video calls, every online activity involves the exchange of these crucial packets. When they fail to reach their destination, users can experience disruptions, slowing down the service or, in severe cases, losing connectivity.
Symptoms of Packet Loss
I’m sure you wonder how to know it’s a packet loss issue before diagnosing and fixing the network lag. Well, some symptoms indicate if it’s a packet loss or not. The symptoms are application-specific mostly, which means you will see and feel particular symptoms when using specific applications.
Online Games:
- In internet gaming, packet loss manifests as “jumpy” or “jerky” movements during network-dependent events. Players may experience disruptions in the flow of the game, making it unplayable due to inconsistent data transmission.
- Packet loss can lead to unusual behavior with timeouts and counters in games. This abnormality can render certain actions ineffective or cause unexpected consequences, creating a frustrating gaming experience.
Telecommunications:
- High levels of packet loss in telecommunications can result in an irritating ‘robot’ effect on voices during calls. Stuttering voices can make conversations challenging, affecting the overall quality of voice communication.
- In video communications, packet loss can lead to frozen frames and stuttering behavior. This visual disruption not only affects the clarity of the video but also hinders the fluidity of the conversation, making it less effective for conveying information.
What are the Causes of Network Packet Loss?
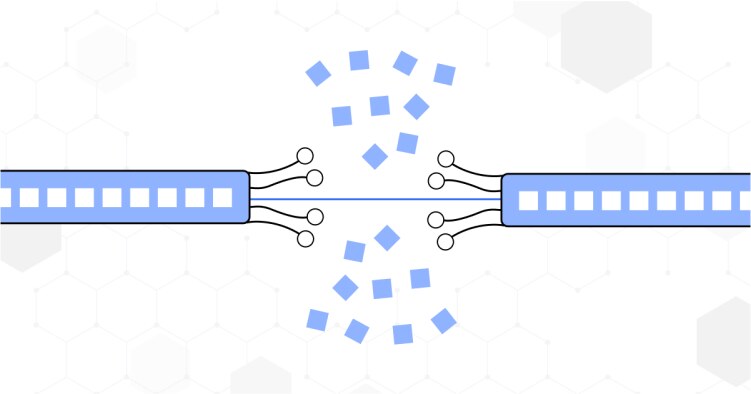
Network packet loss can significantly impact the seamless flow of digital communication. Identifying the root causes of packet loss is crucial for maintaining a robust and reliable network. Let’s look into the key factors contributing to this invisible disruptor:
1. Network Congestion:
When network traffic peaks, similar to rush hour on a congested highway, data packets may experience delays or get dropped. Routers, dealing with limited bandwidth, might discard packets to alleviate congestion.
The distance between network points also adds complexity. Greater distances can introduce bottlenecks, amplifying the likelihood of packet loss. Transcontinental data transmission, for example, faces increased congestion challenges.
2. Faulty Network Hardware:
Damaged cables, outdated routers, or faulty network devices can disrupt the smooth flow of packets. Network interfaces, switches, and routers may drop or delay packets, impacting overall network performance.
Besides, inadequate processing power in layer 3 devices like routers can lead to packet loss. Without sufficient capacity to manage traffic, these devices may struggle, resulting in dropped or delayed packets.
3. Software Bugs:
Bugs or glitches in network software, firmware, or operating systems can introduce unexpected behaviors, including dropped or delayed packets. Regular updates and vigilant monitoring are essential to prevent or rectify high packet loss.
4. Security Breach:
Security measures like firewalls or intrusion detection systems may unintentionally block or filter certain packets, causing packet loss. Misconfigurations or overly strict security settings can disrupt legitimate data transmission.
In rare instances, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack can flood the network with excessive data packets, overwhelming resources and resulting in packet loss. Timely detection and response are critical in such scenarios.
5. Improper Network Configuration:
Incorrect configurations on network devices are one of the major packet loss causes. A single misconfiguration in a switch, for example, could trigger network loops, disrupting the entire system.
Ping and Packet Loss
Alright, let’s dive into more details so that we understand lag, ping, and packet loss in network connectivity. Assessing the performance of a connection involves scrutinizing upload speed, download speed, and ping.
Upload Speed:
This metric gauges how swiftly you can dispatch data packets to others. Whether sending hefty files via email or engaging in video conversations, upload speed, quantified in megabits per second (Mbps), plays a crucial role in efficient data transmission.
Download Speed:
On the other hand, download speed denotes how quickly you can retrieve data packets from the server. Typically designed to outpace upload speeds by default, this parameter, also measured in Mbps, influences the swiftness of accessing online content.
Ping:
The round-trip travel time of the data packet is called ping. Ping emerges as the reaction time of your connection, indicating how promptly you receive a response after sending a request. Crucial in real-time applications like gaming and voice/video calls, ping is measured in milliseconds (ms). A lower ping signifies a more responsive connection.
Ideal Ping and Packet Loss:
An ideal ping sits below 15 ms, ensuring a responsive experience. However, if the ping surpasses 300 ms, a noticeable lag can impede seamless interactions. Despite a seemingly good ping, issues may persist due to packet loss. Even if data reaches the destination server rapidly, some data might not traverse accurately.
How Does Packet Loss Affect Your Network?

Packet loss, a prevalent challenge in today’s interconnected world, significantly affects network performance and operational efficiency. It disrupts the seamless flow of data and increases latency as lost packets require retransmission. Business applications, especially real-time processes like video streaming and VoIP, bear the brunt, leading to a compromised end-user experience.
The financial loss is tangible, with increased operational expenses and productivity challenges. Communication quality also suffers, with even minor losses impacting real-time applications. Moreover, packet loss opens doors to security vulnerabilities, providing opportunities for cyber threats. Encrypted data becomes susceptible to compromise, and unpredictable network behavior emerges as packets experience severe delays. Different applications respond uniquely to packet loss, with real-time processes being notably sensitive.
So, what should you do? To safeguard against these effects, you need to identify and rectify underlying network issues, ensuring uninterrupted and efficient digital communication.
What is Packet Loss with TCP/IP
In TCP/IP, dropped packets get a second chance. If one goes missing, TCP automatically resends it, ensuring data continuity. This process is detailed in RFCs 3366 and 2988. TCP’s congestion control, outlined in RFC 2581, helps avoid data traffic jams. After a set number of ignored packets, TCP assumes the other end might be down.
So, TCP fights packet loss, but the remedy slows things down a bit as it takes time to resend the missing bits. It’s like ensuring your mail reaches its destination, even if the postman has to make a second trip.
Packet Loss with UDP
When it comes to User Datagram Protocol (UDP), lost packets don’t get a second chance automatically. Unlike TCP, which tirelessly resends dropped packets, UDP takes a more laissez-faire approach. It’s commonly employed in real-time streaming applications that can handle a bit of packet loss without any issue.
However, if an application insists on a second shot for lost packets, it’s on its own – or it might consider a shift to the TCP/IP team. In the world of UDP, no automatic packet mulligans are given, and if you want a redo, you’ve got to make it happen yourself or think about changing the protocol to TCP/IP.
How to Diagnose and Detect Packet Loss?

Suppose, you notice the symptoms, but how to detect packet loss to be sure about it before taking the necessary actions? Detecting packet loss is crucial to fixing the issues and maintaining a healthy network. Here are some techniques you can use to detect packet loss.
1. Ping Test: Start with a basic ping test. Ping sends small packets of data to a target server and measures the time it takes for them to return. A high ping time or intermittent timeouts can indicate packet loss.
2. Network Monitoring Tools: You can deploy a network monitoring tool to detect high packet loss. These tools provide detailed insights.
3. Command-Line Tools: Command-line tools like PathPing (Windows) and MTR (Linux/Unix) offer comprehensive diagnostic information, including packet loss rates and network latency.
4. Analyzing Network Devices: Check network devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls for hardware failures, misconfigurations, or overloaded capacities. All of these can be a source of what causes packet loss.
5. Packet Loss Patterns: Analyze packet loss patterns to determine if they are consistent across specific routes, periods, or types of traffic. This information can help isolate the root cause more effectively.
Deep Packet Inspection
If your organization’s network is a bustling highway with countless vehicles moving in different directions every day, Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) acts like a traffic controller. It carefully scrutinizes each vehicle to ensure smooth and secure traffic flow.
DPI goes beyond surface-level analysis. It dives deep into the contents of network traffic, examining every packet that passes through. So, what are the contents of a network packet?
Each packet has three main parts:
- Header: This is like the packet’s ID card, containing crucial instructions and details such as where it’s from, where it’s going, and what type of data it carries.
- Payload: Consider this the heart of the packet, where the actual data resides. It could be anything from emails and images to videos and documents.
- Trailer: Think of the trailer as the packet’s farewell note, signaling the end of its journey.
DPI’s job is to analyze these parts thoroughly. It looks for specific data or code indicating threats or policy violations. For instance, it can identify and block packets containing malware or inappropriate content, ensuring a safer network environment. Network administrators rely heavily on DPI to maintain network integrity and security.
Monitoring Network Packet Loss
Every network may face delays and lags to some extent, but how to detect a high packet loss? Monitoring packet loss is more important than anything for maintaining network health and performance. By regularly scanning network devices and infrastructure, administrators can gauge the health of routers, switches, and other components. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention to prevent potential data loss and degradation of network performance.
The ability to measure packet loss accurately is paramount in identifying anomalies and addressing them promptly. Implementing robust monitoring tools enables administrators to track packet loss metrics, identify trends, and pinpoint areas of concern within the network topology.
Acceptable Packet Loss
You can determine if it’s a high packet loss or within the acceptable limit by measuring the percentage of data loss. Acceptable packet loss varies based on network type and application. In a LAN, less than 1% packet loss is generally tolerable, while in a WAN, up to 3% may be acceptable. For most applications, 1%-2% packet loss is manageable, but rates above 5% can notably impact performance.
In real-time applications like VoIP, occasional packet loss may not affect quality, but losses between 5% and 10% can significantly degrade it. For streaming audio or video, less than 1% packet loss is considered good, while 1%-2.5% is acceptable. Despite efforts to minimize packet loss, some level of tolerance is built into protocols to maintain functionality.
What is Packet Loss Fixing? How to Do It?
Well, now you know what packet loss is and how to detect packet loss in your network, but you have to fix the issue, right? High packet loss can significantly affect your VoIP calling or online gaming experience. Fixing/reducing packet loss can resolve the problem.
Fixing packet loss involves various troubleshooting steps, including analyzing network performance, upgrading hardware, optimizing network configurations, and implementing security measures. The goal of packet loss fixing is to minimize disruptions to network communication, enhance data transmission efficiency, and ensure a reliable network infrastructure.
Take the following steps to reduce network packet loss:
1. Restart the System: Rebooting devices can resolve temporary glitches or software issues that may cause packet loss. It clears system memory, refreshes connections, and restarts processes, often improving network performance.
2. Do a Ping Test: Conducting a ping test helps assess the network’s responsiveness and identifies potential packet loss issues. By sending ICMP packets to a specific destination and measuring the round-trip time, you can determine if packets are being lost or delayed.
3. Measure Packet Loss: Use network monitoring tools to measure packet loss accurately. Real-time and historical packet loss data provide insights into network performance, helping diagnose underlying issues and implement targeted solutions.
4. Upgrade Hardware: Outdated or inefficient hardware can contribute to packet loss. Upgrading routers, switches, and network cards to newer, more reliable models can enhance network stability and reduce the occurrence of packet loss.
5. Try a Wired Connection: Wired Ethernet connections are generally more stable than wireless connections, reducing the risk of packet loss due to signal interference or fluctuations. Switching to a wired connection can mitigate packet loss issues, especially in environments with high network traffic.
6. Optimize Network Traffic: Implement Quality of Service (QoS) settings to prioritize critical traffic and allocate bandwidth effectively. By managing network resources and minimizing congestion, you can reduce the likelihood of packet loss and ensure smooth data transmission.
7. Strengthen Security: Enhance network security measures to prevent unauthorized access and potential cyber threats that could lead to packet loss. Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption protocols to safeguard network integrity and minimize disruptions.
How to Prevent Packet Loss Issues?
Prevention is better than cure, isn’t it? Packet loss can occur due to various reasons such as network congestion, hardware issues, or security threats. In the world of digital connectivity, where seamless data transmission is mandatory, packet loss poses a significant challenge.
However, by understanding the causes and implementing proactive strategies, organizations can effectively prevent and mitigate the impact of packet loss on their networks. Follow these essential techniques and best practices to prevent packet loss issues and maintain optimal network performance.
- Regularly monitor network performance using specialized tools
- Check physical network connections for damage
- Audit network configurations to avoid loops and bottlenecks
- Prioritize wired connections over wireless ones
- Maintain robust security with antivirus and antimalware programs
Conclusion
We’ve covered everything you need to know what is packet loss, how to detect packet loss in your network, and how you can fix it. However, depending on your network type and functionalities you may need to contact your ISP or an expert network professional to resolve critical packet loss issues.
While complete elimination of packet loss may be unattainable, a proactive approach to prevention significantly enhances network resilience and ensures seamless operations. By embracing the strategies we suggested, organizations can confidently navigate the complexities of network communication and minimize packet loss to an acceptable level.