
In today’s threat-filled digital world, security is a key non-negotiable for any business, right? Every enterprise needs a robust and effective security mechanism to protect its network from hackers and cyber attackers. While Firewalls are among the first security mechanisms, with time and change, SBCs or Session Border Controllers have become a more popular choice. But what exactly are a firewall and an SBC and which one should you be using for your business? If you’re curious to learn about SBC vs Firewall, then read until the end.
This post provides you with a comprehensive comparison between the two popular network devices – SBCs vs Firewalls.
Let’s jump right into it!
What is a Firewall?
As the term indicates, a firewall is a network security system that typically establishes a barrier between two networks. It monitors and controls all the incoming and outgoing traffic by making use of pre-configured security rules or protocols.
What Does a Firewall Do?
A firewall lets certain things come inside the network while keeping others out, just like a security guard. It is a static technology which means firewalls can either open up or shut down interfaces.
Key Features of a Firewall
Take a look at some of the key features of a firewall to understand how it provides primary protection to your network from unauthorized access and malicious threats.
- Packet Filtering
The most basic feature of a firewall is packet filtering. As the term implies, it inspects each network packet to decide whether it should be allowed to pass or blocked based on its IP address or some predefined criteria.
- Stateful Inspection
It is a feature within the firewalls that tracks the state of active network connections to make informed decisions about incoming and outgoing traffic. This type of inspection offers a deeper level of security because traffic patterns are being analyzed and only those associated with active sessions are allowed.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDP)
Firewalls with IDP systems are capable of monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities. By doing so, they detect and block malicious threats and intrusions such as malware and hacking attacks in real time.
- Proxy Service
Firewalls with proxy support act as intermediary between users and the internet. By preventing networks from directly connecting with other systems and inspecting all the incoming and outgoing traffic before passing it through, proxy service hides internal network addresses and thus prevents direct attacks on your systems.
- Virtual Private Network Support
Firewalls with VPN support facilitate users with secure remote access to the network. By encrypting the traffic, it ensures secure communication for remote users.
- Application Control
Firewalls with application control features allow organizations to enforce security at a more granular level. Rather than relying on IP addresses and ports, this feature monitors and controls applications accessing the network or being accessed on the network. By doing so, it helps prevent unauthorized use of resources.
Use Cases of Firewalls
Firewalls are a versatile and essential security tool with a wide range of applications across various industries and environments. Here are some common use cases of firewalls
- Network Perimeter Defense
Firewalls are extensively used to protect corporate networks from external threats. By placing a firewall at an organization’s network perimeter, the incoming and outgoing traffic gets filtered and blocks unauthorized access, malware attacks, and hacking attempts.
- Secure Remote Access
Firewalls with VPN support are used to allow remote employees to connect securely to the corporate networks. The firewall filters traffic to block malicious attacks and keeps the communication encrypted.
- Data Center Security
Firewalls are also an integral part of large data centers to protect data and infrastructure within them. By monitoring the traffic between servers, firewalls prevent unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Internal Network Segmentation
To protect against insider threats, firewalls are used to segment internal networks thus controlling access between different internal departments. Through this segmentation, organizations can ensure that only authorized users have access to specific parts of the network.
- Logging and Audit Capabilities
Administrators make use of logs of network events which are stored and maintained by firewalls to detect patterns and refine security rules. It is essential to update these rules regularly to stay ahead of the evolving cyber threats.
What is a Session Border Controller?
SBC or Session Border Controllers are much more advanced when it comes to traffic management. While Firewalls are able to work up to 4 layers of the OSI model of a network, SBCs work all the way up to layer 7. SBCs thus act as a single network management solution that addresses all security and application concerns.
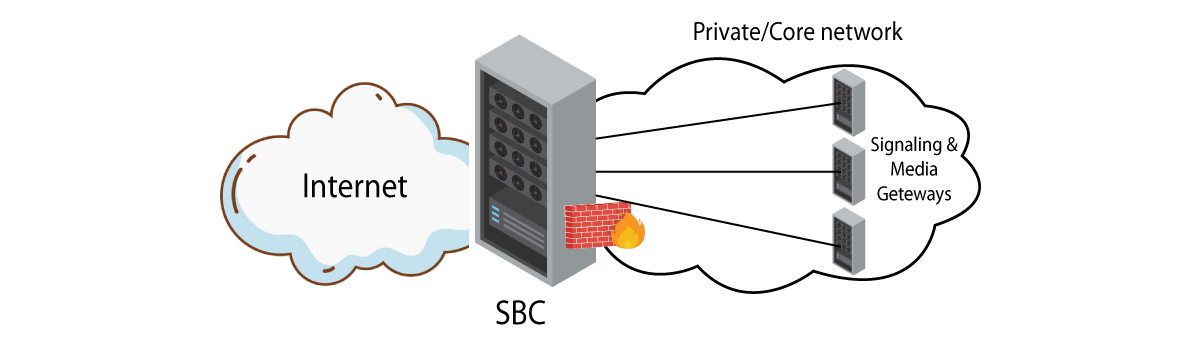
When the internet came into existence, it offered very little protection to data. Hackers, cyber attackers, and spammers could easily get into a network and steal or misuse data shared over the cloud.
Firewalls were introduced to offer network security and they did their job well for a long time, but eventually failed to meet the security requirements of the ever-growing networks. Firewalls have control only over the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th layers of the OSI model i.e. Data Link Layer, Network Layer and Transport Layer. However, with constant changes being made in security protocols and system updates, changes are introduced in the 3rd and 4th layers of the OSI model. But layer 5 to layer 7 remain unchanged as firewalls could not access those. This results in some significant quality issues in real-time communications such as echo in voice and video communication.
As the technologies advanced, so did the tactics of hackers who figured out one way or the other to execute their attacks.
SBCs perform their functions to ensure that phone calls and video systems remain free of any quality issues and thus end users can have a smooth communication experience. Moreover, SBCs ensure that the quality of communication remains unaffected even when additional people are conferenced in. From a security perspective, SBCs make use of AI to detect any malicious parties entering the system. It makes use of static and dynamic ACLs i.e. Access Control Lists to define who is authorized to come in and who is not.
Key Features of SBC
- Encryption and Decryption
SBCs support industry-standard encryption protocols such as SRTP and TLS to encrypt voice and signaling traffic thus ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
- Quality of Service
SBCs implement various QoS techniques like jitter buffering and packet prioritization to ensure that voice traffic receives the required bandwidth and priority over other network traffic.
- NAT Traversal
SBCs enable VoIP communication across networks through NAT Traversal i.e. modify signaling and media packets to include the SBC’s public IP and port information
- Load Balancing
Through load balancing i.e. distributing traffic across multiple servers, SBCs ensures optimal resource utilization and prevent overload.
- Failovers
SBCs come with built-in redundancy mechanisms that help them maintain uninterrupted services. This happens as systems automatically switch to backup systems in the event of hardware or software issues.
- Regulatory Compliance
SBCs can be configured to comply with various regulatory standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS.
Applications of SBC
Session Border Controllers are extensively used in VoIP and SIP-based communications for efficient management and security. Various industries such as healthcare, and online gaming make use of SBCs to prevent attacks and ensure security.
Key Differences Between SBC and Firewall
Now let us understand the difference between SBC and Firewall in terms of various parameters. This will help you select the right one for your business.
Communication
Session Border Controllers perform the job of managing and controlling real-time voice and video communication sessions. However, Firewalls can either block or allow the data communication flow.
Implementation
The implementation of Session Border Controller takes place as a Back-to-Back-User-Agent i.e. B2BUA. On the other hand, Firewalls are implemented as proxy servers.
Media & Signaling
Session Border Controllers are actively involved in the processing of both signaling and media paths. Whereas in the case of Firewalls, there is no involvement in the audio/video streams or the RTP media path.
OSI Layers
Session Border Controllers can deal with any layer of the OSI stack. However, Firewalls can only look at traffic on layers 2, 3 & 4 of the OSI model.
Topology Hiding
A major parameter that differentiates SBCs from Firewalls is Topology Hiding. SBCs perform Topology Hiding by removing or hiding basic internal network information from the signaling stream. This is done to prevent internal network details from being propagated to untrusted networks.
Codec Transcoding
Another way SBCs stand out is their ability to perform interworking between incompatible codecs, protocols, and SIP variants. SBCs act as real-time translators throughout each session to ascertain that there is no loss of features.
Functionality
The main role of Firewalls is to provide security to the network while Session Border Controllers go well beyond the security focus of the firewalls. Besides security, SBCs also ensure that the communication traffic is delivered via the optimum route by using intelligent call routing. By doing so, SBCs ensure QoS i.e. Quality of Service, and hence boost customer satisfaction.
It is important to understand the functions of both firewalls and SBCs in controlling traffic and implementing security policies. Only then we can be successful in creating a network design that ensures the protection of the vital communication systems as well as providing the desired level of QoS to users.
|
Feature |
SBC |
Firewall |
|
Primary Function |
Managing and securing real-time communication sessions (voice, video) |
Protecting networks from unauthorized access and malicious attacks |
|
Layer of Operation |
Application Layer (Layer 7 of OSI model) |
Network and Transport Layers (Layers 3/4 of OSI model) |
|
Traffic Managed |
Real-time communication (voice, video) |
All types of network traffic (HTTP, FTP, VoIP, etc.) |
|
NAT Capabilities |
Optimized for NAT traversal, handles complex VoIP NAT scenarios |
Can perform basic NAT but not optimized for VoIP |
|
Signaling Protocols |
Supports SIP, H.323, RTP and other VoIP signaling protocols |
General protocol handling (TCP, UDP, HTTP, etc.); does not typically support VoIP signaling protocols |
|
Media Processing |
Handles media transcoding, transrating, and quality of service (QoS) |
Does not typically handle media processing |
|
Protocol Translation |
Translates between different VoIP protocols (SIP to H.323) |
No protocol translation |
|
Encryption |
Encrypts VoIP signaling and media (SRTP, TLS) | Handles encryption for general data traffic (e.g., HTTPS) |
|
Security Features |
Provides security features like SIP authentication, anti-spam, and call policy enforcement |
Offers general network security features like packet filtering, intrusion detection, and VPN support |
| DDoS Protection |
Protects VoIP services from SIP-based DDoS attacks |
General DDoS protection for all network traffic |
|
Deployment |
Typically deployed at the edge of the network or between different communication networks |
Often deployed at the network perimeter |
|
Use Cases |
VoIP, video conferencing, unified communications |
General network security, remote access, and application control |
Complementary Role of SBC and Firewall
It is important to understand that SBCs do not replace firewalls. With all the differences in their features and functionalities, there are several instances where an SBC compliments a firewall. This means they both often work together in a complementary manner. Let’s have a look at how they make a strong partnership:
- Security
Firewalls act as the first line of defense. They are used as an initial security barrier to protect networks from external threats, usually malware, and DoS attacks. Session Border Controllers, on the other hand, focus on securing real-time communication sessions. They are good at preventing attacks like SIP flooding, call highjacking, and eavesdropping.
- Communication Management
Session Border Controllers primarily handle voice and video communication sessions in real time. They employ certain services like QoS, call admission control, and NAT traversal to ensure sessions are efficiently managed, prioritized, and secured. A firewall does not directly play a role in these functions but plays a supporting role by filtering out general malicious traffic before it reaches the SBC.
- Network Integration
SBCs often play the role of gatekeepers that bridge different types of communication networks, such as the PSTN and VoIP networks. SBCs ensure seamless communication between devices on VoIP and PSTN networks by translating signaling protocols and media formats used by these different devices.
When integrating PSTN and VoIP networks, SBCs create interfaces that connect the internal network to the external world. At these interfaces, unauthorized access or security breaches could occur. This is where a firewall could help. As it sits at the boundary of the network, it offers an additional layer of security by performing traffic filtration, blocking unwanted external access, and preventing network attacks.
SBC vs Firewall: Which One Do You Need?
When to Use a Firewall?
- For General Network Protection
- Within Non-VoIP Environments
- Intrusion Prevention
When to Use an SBC?
- Within VoIP and Unified Communications Environments
- For Regulatory Compliance
- To protect Real-time Communication
- For Multi-network VoIP Integration
About REVE SBC
REVE SBC is a robust and scalable Class 4 Softswitch platform designed and developed for communication service providers. It comes with a powerful distributed architecture that ensures network availability and resiliency against cyber threats. Integrated with a real-time billing platform that works on intelligent routing, REVE SBC adds more scalability to your IP wholesale business.
Do You Need Both SBC and Firewall?
There are several scenarios (a few I have mentioned above) where using both an SBC and a firewall together is the best approach. While a firewall offers primary defense for the overall network, the SBC takes it to an advanced level. By combining the strengths of both firewalls and SBCs, organizations can protect and manage their networks through a layered approach.
SBC vs Firewall: Conclusion
We all know that the security of VoIP networks is important and many of us are under the perception that a Firewall offers almost equal security as that of an SBC. So the contemplation of whether one really needs to purchase an SBC to secure their business network remains there. Clearly, Session Border Controllers are the superior choice for ensuring secure, reliable, and high-quality IP-based interactive communications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is an SBC the same as Firewall?
No, an SBC or Session Border Controller is different from a firewall as they serve different purposes. Though both are network devices, an SBC is specially designed to manage and secure real-time communication such as VoIP. On the other side, a firewall provides general network security by performing traffic filtering and blocking unauthorized access.
Which one is better: SBC or Firewall?
Both SBC and Firewall are valuable tools. The choice for ‘better’ depends upon your specific requirements. SBCs are great for securing and managing VoIP traffic. However, if your primary concern is general network protection, then a firewall is more suitable.
Can a Firewall and SBC be used together?
Yes, SBCs and Firewalls can be used together. They should be used together to provide comprehensive network security and communication management they offer when combined. While an SBC can manage and secure real-time communication sessions, a firewall can protect the SBC from external threats.
How do SBCs ensure low latency and high quality of service (QoS) for real-time communications?
SBCs employ different techniques to ensure low latency and high QoS such as prioritizing real-time traffic over other types of data, transcoding and transrating to adapt media to network conditions, managing bandwidth, and using redundant configurations to ensure high availability.
Can an SBC be configured to prioritize specific types of VoIP traffic?
Yes, you can configure an SBC to prioritize certain types of VoIP traffic. By implementing Quality of Service policies, you can assign different levels of priority to different types of traffic. For example, real-time communication such as voice traffic can be given higher priority over data traffic to ensure that call quality is not affected by network congestion.
Note- This post has been updated on 29-11-2024.






















