Do you feel the rapid changes in the ever-evolving communication system we use regularly? Surely you do. In enterprise communications, the Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC) is crucial in ensuring security, interoperability, and quality. As businesses transition from traditional PBX systems to VoIP, Unified Communications (UC), and cloud services, the ESBC emerges as a guardian, protecting the integrity and efficiency of these modern communication networks.
Today’s communication landscape extends beyond voice calls to encompass video conferencing, team collaboration, and instant messaging within Unified Communication and Collaboration (UCC) ecosystems. At the heart of this convergence lies the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP), facilitating communication sessions across diverse endpoints. However, challenges such as vendor interoperability and internet security necessitate the Session Border Controller (SBC) presence.
In this blog, we explore the significance of Enterprise Session Border Controllers, examining their types, functions, and the benefits they bring to organizations navigating the complexities of real-time communication. So, let’s unravel the essence of ESBCs and their transformative impact on modern enterprise communication networks.
What is an Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC)?
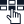
An Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC) is a vital enterprise network element, managing communication traffic between internal systems and external networks like the Internet and SIP trunk providers. It acts as a communication controller, facilitating connections with the public telephone network, cloud services, and premise-based systems such as legacy PBXs and UC platforms like Microsoft Teams.
ESBCs, available as dedicated hardware or software, oversee the initiation, conduct, and termination of sessions within VoIP networks. They ensure secure communication flow, enforce policies, and enhance network security and routing. ESBCs are essential for solutions like MS Teams Direct Routing, enabling proper call routing while meeting compatibility requirements.
Deployed on both carrier and enterprise sides, Enterprise SBCs function as session traffic firewalls, applying Quality of Service rules and protecting against threats. They work as sophisticated gatekeepers ensuring the integrity and security of enterprise communication networks amid the challenges of real-time communication.
An Enterprise Session Border Controller enables:
- Secure SIP trunking
- Integration of VoIP and UC networks
- Implementation of IP contact centers
- Accessibility to cloud and hosted IP communication services
- Connectivity for remote workers and branch offices
How Do Session Border Controllers Work?
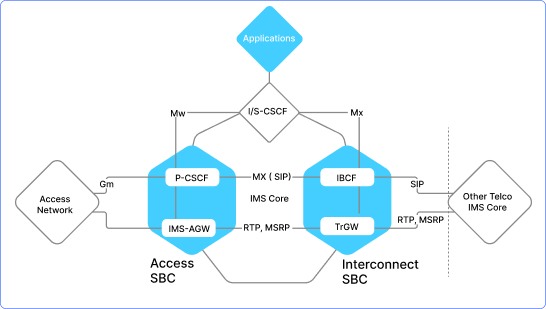
SBC’s working process won’t be as complex as it seems once we explain it to you. Session Border Controllers (SBCs) are crucial in managing the signals and media streams involved in initiating, conducting, and terminating phone calls and interactive media encounters. They ensure security by implementing features like call admission control, toll fraud detection, and denial-of-service (DoS) protection. SBCs also translate protocols, ensuring that communication between different systems remains seamless.
In Microsoft Teams Direct Routing implementations, the SBC resides in the cloud at the network edge between the Microsoft Phone System and the managed provider’s network. When users make calls from Teams-enabled devices, the data flows through the Internet to the Microsoft Phone System and then to the SBC. The SBC routes the session data to the public network, ensuring interoperability across different vendors by normalizing signaling stream headers and messages.
SBCs facilitate connections between various voice or video codecs like H.323, g.711, and g.729, and may transcode signals to match network capabilities. This ensures seamless communication across complex and multi-vendor telephony infrastructures. Carriers route calls across the PSTN network to their destinations, with Microsoft acting as the carrier for Microsoft Calling Plans and third-party providers offering global carrier networks for MS Teams Direct Routing.
Organizations typically rely on managed service providers or Microsoft to deploy and maintain these devices. Managed service providers configure the SBC in Direct Routing implementations, simplifying the process for organizations. SBCs thus serve as critical components in ensuring secure, interoperable, and efficient communication within modern enterprise networks.
Redefining Enterprise Communications
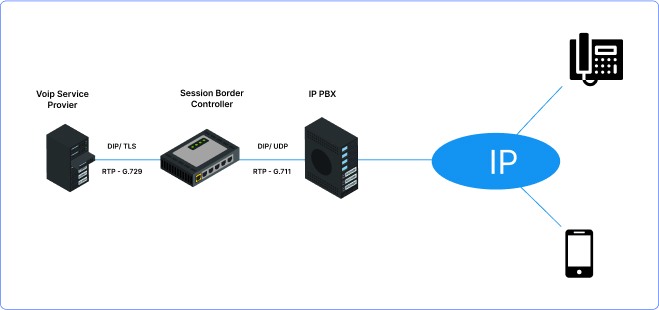
Rapid advancements in mobile technology and the widespread adoption of Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) and rich media communications are reshaping business communications. The traditional office telephone system is nearing its end. Enterprise communications are transforming, shifting from time-division multiplexing (TDM) to IP, moving from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based solutions, and evolving from voice-centric to multimodal communications.
This shift marks the end of the era of traditional office telephone systems, as enterprise communications transition from time-division multiplexing (TDM) to IP-based solutions, from on-premises infrastructure to cloud-based platforms, and from voice-centric to multimodal communication modalities.
Several technological trends are driving this shift in enterprise communications and making IT professionals rethink their strategies—
- Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) Initiatives
The distinction between personal and work devices is diminishing. Unified Communications (UC) solutions are replacing traditional phone calls with multimedia interactions that integrate voice, video, chat, and web collaboration. Enterprises are leveraging HD videoconferencing and telepresence systems to enable remote meetings and enhance productivity for mobile workers.
- Unified Communications
The emergence of cloud services offers a diverse range of solutions, including videoconferencing services, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and contact center services. These cloud-based solutions empower IT organizations to reduce capital equipment costs, simplify service deployment, and focus on business innovation rather than managing telecommunications infrastructure.
- Communications-enabled Business Processes
It embeds UC capabilities directly into business processes and applications. By orchestrating real-time communication sessions with presence information and business rules, organizations enhance decision-making, employee productivity, and customer service.
Functions of an Enterprise Session Border Controller
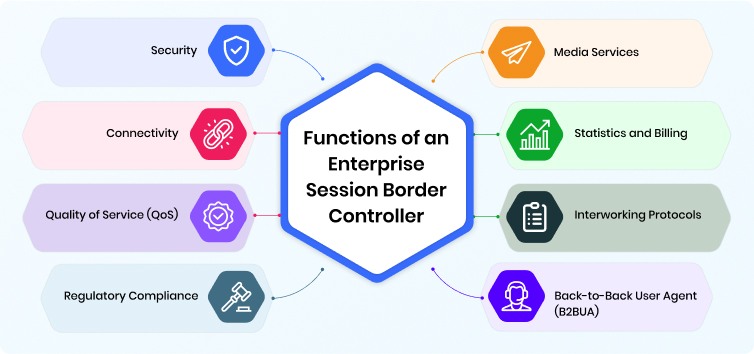
It’s the functions of an ESBC that are transforming enterprise communications, right? Here, we’ve covered the major Enterprise Session Border Controller capabilities critical for modern enterprise communication networks:
1. Security:
ESBCs ensure network security by protecting against a variety of threats including denial-of-service (DoS) attacks, distributed DoS (DDoS) attacks, and toll fraud. They achieve this through robust security measures such as encryption of signaling and media streams, safeguarding against impersonation, and ensuring the confidentiality of communication sessions.
2. Connectivity:
Enterprise SBCs enable seamless communication between different parts of the network by employing various techniques such as NAT traversal, SIP normalization, IPv4 to IPv6 interworking, and VPN connectivity. These capabilities ensure that communication flows smoothly across diverse network environments.
3. Quality of Service (QoS):
Maintaining high-quality communication is essential for enterprise networks. ESBCs enforce QoS policies by implementing traffic policing, resource allocation, rate limiting, call admission control, and ToS/DSCP bit setting. These measures prioritize critical communication flows and ensure optimal performance across the network.
4. Regulatory Compliance:
Compliance with regulatory requirements is a crucial aspect of enterprise communication. Enterprise SBCs support regulatory standards by facilitating features such as emergency call prioritization and lawful interception, ensuring that organizations meet legal obligations and standards.
5. Media Services:
Modern ESBCs incorporate built-in digital signal processors (DSPs) to provide advanced media services. These services include DTMF relay, media transcoding to support different codecs, tones, and announcements, and comprehensive support for voice and video calls.
6. Statistics and Billing:
Serving as natural traffic control points within the network, Enterprise Session Border Controllers gather valuable statistics and usage-based information. This data facilitates billing processes, network analysis, and optimization efforts, providing insights into communication patterns and resource utilization.
7. Interworking Protocols:
ESBCs facilitate interoperability among diverse communication protocols and codecs. They enable seamless translation between SIP, H.323, and other formats, ensuring that communication remains uninterrupted and compatible across different network environments.
8. Back-to-Back User Agent (B2BUA):
Acting as B2BUAs, ESBCs control SIP signaling between separate endpoints within the network. They manage requests, process traffic across SIP networks, and ensure efficient routing and handling of communication sessions.
What Does an ESBC Do to Facilitate Enterprise Communication?
An Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC) serves as a vital component in ensuring smooth enterprise communication. It ensures security by protecting networks, facilitates interoperability by mediating between different communication systems, enforces Quality of Service (QoS) policies, and manages call admission control for optimal performance.
ESBCs also assist enterprises in adhering to regulatory requirements by supporting features like emergency call prioritization and lawful interception. We already talked about all these ESBC functions. Now let’s point out the major contributions of ESBCs to enterprise communication.
Protects and Controls IP Communications
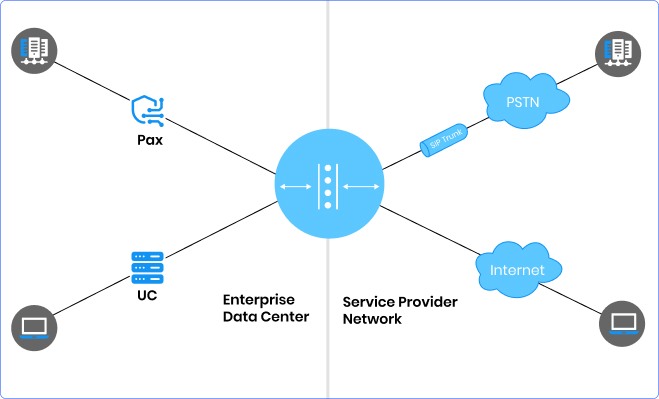
Enterprise Session Border Controllers (ESBCs) manage the complexities of real-time IP communications across network borders. Positioned in the demilitarized zone (DMZ), a SIP Session Border Controller operates at the session layer, handling traffic primarily using SIP protocols. They terminate and reoriginate each communication session, enabling thorough traffic inspection and policy enforcement.
These controllers address security, interoperability, and service quality concerns in VoIP, UC, and BYOD initiatives. As enterprises transition to IP communications, ESBCs ensure efficient IT asset management and uphold communication quality and security standards across network boundaries.
Enterprise Session Border Controllers Do More than Firewalls

IP communication sessions involve both signaling (for session setup and control) and media (voice and video) components, each flowing through different IP protocols and paths.
- Firewalls typically offer basic SIP support through access control lists (ACLs) that permit or deny SIP traffic based on addressing information. However, firewalls lack active control over real-time IP communication sessions, unlike ESBCs.
- In SIP terminology, a SIP firewall functions as a proxy server, managing SIP signaling but not the RTP media path. Conversely, an ESBC operates as a back-to-back user agent (B2BUA), actively handling signaling and media paths.
- An ESBC terminates a session from one SIP entity and initiates a separate session with another, allowing inspection and manipulation of entire sessions to enforce security policies and manage communications efficiently.
- Unlike firewalls, ESBCs maintain a session state and control both SIP signaling and associated RTP media streams. For instance, ESBCs keep pinholes open throughout a session, ensuring continuity, whereas firewalls may disrupt sessions by closing and reopening pinholes with different port numbers.
Builds a Foundation for Scalable, Secure Communications

Interoperability challenges often arise when extending IP communications across network borders due to the flexibility of SIP specifications. Enterprise SBCs alleviate these concerns by facilitating scalable UC architectures while ensuring control and security. They manage session states, manipulate RTP media streams and SIP signaling, and enforce comprehensive security controls across diverse networks.
Positioned at the network edge, Enterprise Session Border Controllers delineate external services, establishing distinct security perimeters. They centralize real-time communications traffic, enabling classification, prioritization, and bandwidth allocation before hand-off to service providers. This centralized control supports SLA monitoring and diverse applications.
Building a secure, adaptable communications infrastructure amidst evolving technologies and regulatory demands remains challenging for IT managers, particularly with limited resources.
Benefits of Using an ESBC
Alright, what are the core benefits you get by using an ESBC? Here are some highlights you can check and it will help you to get a better understanding of this network element.
1. Greater IP Network Security:
Enterprise SBCs offer specialized security features to safeguard against various threats including denial-of-service (DoS) attacks and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. They ensure privacy and confidentiality through IP address and topology concealment, encryption capabilities, and access control.
2. Platform for Interoperability:
They facilitate seamless communication across diverse networks by providing extensive protocol normalization and mediation functions. ESBCs also mitigate multivendor interoperability issues and offer comprehensive network address translation (NAT) and firewall traversal features.
3. Increased Service Quality and Availability:
ESBCs ensure PSTN-like availability and service quality by balancing loads across trunks, rerouting sessions during network problems, and providing QoS marking and admission control capabilities.
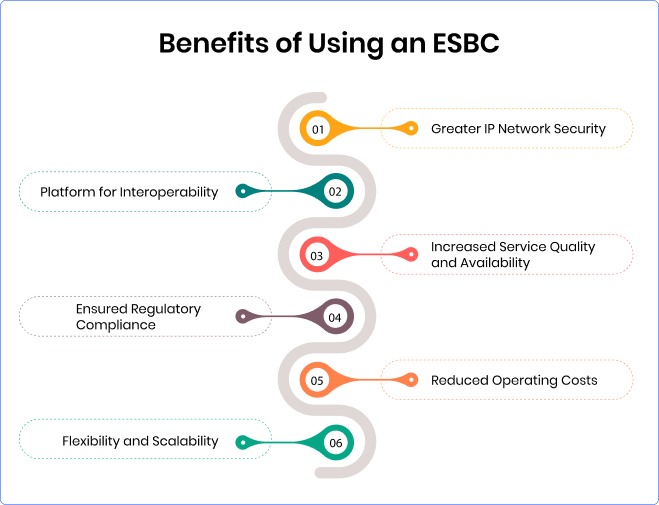
4. Ensured Regulatory Compliance:
Organizations rely on ESBCs to maintain regulatory standards, ensuring communication confidentiality, integrity, and emergency service prioritization while recording essential calls to comply with industry regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
5. Reduced Operating Costs:
By implementing Enterprise Session Border Controllers, network infrastructure becomes more efficient, reducing the need for troubleshooting and centralizing monitoring efforts. Additionally, transitioning to cloud-based solutions provides cost savings by decreasing hardware investments and maintenance expenses.
6. Flexibility and Scalability:
Providing adaptable solutions to accommodate growing traffic volumes, ESBCs empower businesses to navigate evolving organizational needs and technological advancements seamlessly, ensuring scalability and operational efficiency.
Enterprise Session Border Controller Market & Growth Opportunities
The ‘Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC) Market’ is anticipated to experience substantial expansion in the foreseeable future, driven mainly by the escalating demand for Next Generation Network (NGN), IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS), and related technologies. Market segmentation encompasses Session Capacity categories:
- Greater than 300
- From 300 to 5000 and
- Over 5000 sessions
The in-depth research and analysis offered in the Enterprise Session Border Controller Market Reports indicate a remarkable annual growth rate (2024 – 2030) for the ESBC market.
Which regions are at the forefront of the Enterprise Session Border Controller (ESBC) Market?
- North America: United States, Canada, and Mexico.
- Europe: Germany, the UK, France, Italy, Russia, Turkey, and more.
- Asia-Pacific: China, Japan, Korea, India, Australia, Indonesia, Thailand, the Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam, and others.
- South America: Brazil, Argentina, Colombia
- Middle East and Africa: Saudi Arabia, UAE, Egypt, Nigeria, South Africa
Conclusion
Before we wrap up, I would like to remind you how crucial Enterprise Session Border Controllers are in modern IP communication. They are pivotal in modernizing communication infrastructures, offering enhanced security, interoperability, and quality of service. ESBC’s deployment enhances network operations, reduces costs, and ensures regulatory compliance.
As organizations increasingly adopt IP-based communications, ESBCs emerge as critical components, facilitating seamless connectivity and enabling efficient management of real-time communication sessions. Their role is poised to expand further as businesses prioritize secure and efficient communication networks in an evolving digital landscape.