Ever wondered how you can scroll through your favorite fitness videos, send emails, and do online banking all at once, without everything turning into a chaotic digital mess? It’s all because of the numeric maestros of the networking world- Port Numbers. Didn’t know what these are? Well, there are over 65,000 ports available each with its own unique port number. Through this blog, we will be cracking the code of – what is a port number and learning everything about port numbers with examples. I will also explain how you can identify the active port numbers on your device.
Let’s dive in!
What is a Port Number in Networking?
A port number is a 16-digit number that acts as a unique identifier for a connection endpoint or a service running on a host. Let’s consider an example for easy understanding.
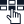
Suppose you have different services running on your computer like your email, web browser, instant chat app, etc. Now each service you use has its own port number. When you browse a website by typing the web address and hitting enter, your web browser sends a request to get access to the website using port number 80. Likewise, when you open your email client to send an email, it uses port number 25 to send your message and as you refresh to check for new emails, the client uses port number 110. Further, as you open your instant chat app to talk with a friend in real-time, the app communicates using port number 6667.
So, each service you use has its own specific port number. When your device i.e. your computer sends or receives data, it knows which door (port number) to use based on the service you’re accessing.
Insight: Port Numbers in networking are logical endpoints which is why they are often referred to as Logical Ports as well. Here the term “logical” emphasizes that these ports are conceptual markers or software-defined addresses and not physical connections.
Which Layer are Ports in the OSI Model?
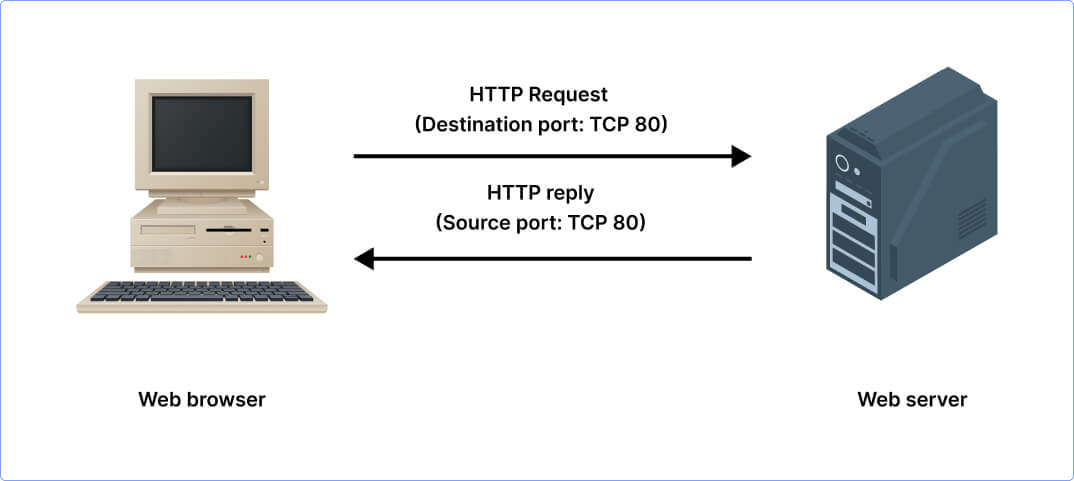
The OSI model is a conceptual model that represents how network communications work. This model has 7 layers shown in the above image. Ports are associated with the Transport Layer i.e. Layer 4 of the OSI model. The Transport Layer primarily makes use of 2 protocols – TCP and UDP. These protocols are needed to specify which port a packet should go to. In the header section of TCP and UDP, the information about port numbers is defined.
How Do Port Numbers Work?
To manage and route data on networks, here’s how port numbers play their part:
Step 1: Application Assignment
Each application that runs on a computer is typically assigned a port number, which acts as a unique identifier. However, some operating systems use dynamic port allocation, where the port number is assigned automatically.
Step 2: Server-Side Listening for Connections
A server application often listens on multiple port numbers to handle different types of requests or connections. For example, a web server might listen on port 80 for HTTP requests, port 443 for HTTPS requests, and other ports for additional services.
Step 3: Incoming Connection From Client-Side
When a client-side application wants to connect with the server application, it sends a message to the server application’s IP address, specifying the port number. This tells the server which service or application to route the request to.
Step 4: Connection Establishment
The server checks the specified port number and if a match is found, it accepts the connection request. Now a communication channel gets established with the client application.
Step 5: Data Exchange
The client-side application starts sending data to the server application. This could be a request for a web page for file transfer. The request is processed by the server and it sends a response back to the client application. Till the time the requested task is executed, the exchange of data continues.
Step 6: Multiple Connections
Each port number on a device is like a separate channel for communication. This is why multiple applications can communicate independently on a device without interfering with one another.
Step 7: Connection Termination
When the data transmission is complete, the client or server decides to end the connection by sending a termination signal. The other party acknowledges the termination request and the connection is closed. The allocated port numbers become available for reuse by other applications.
Example of Port Number Working
Suppose Alex sends Emma a high-resolution image using the HTTP on port 80. Emma’s web browser listens for incoming data at port 80, processes it, and displays it. All this happens seamlessly. Simultaneously, Alex also shares a spreadsheet with Emma using FTP on port 21. Emma’s computer efficiently receives the file using the FTP service and stores it. Now comes a twist. Alex mistakenly tries to send a video file to Emma using SMTP on port 25. This port is typically reserved for email applications. If in case, Emma’s device receives the file and transfers it to the email application, then the email application will have no clue about what to do with the file.
In short, each application on Emma’s computer is assigned to a unique port, ensuring that data received on that port is directed to the appropriate application capable of interpreting and processing it.
What is the Difference Between an IP Address and a Port Number?
In the context of networking, it is important to learn the difference between an IP address and a port number. It will help you understand how data is directed within a network. So let’s take a look:
An IP address identifies a machine in an IP network and is used to identify the destination address of a packet. On the other hand, a port number identifies a certain service or application on a system.
What is the Difference Between a Proxy Server Address and a Port Number?
A Proxy Server Address is the IP address that identifies the location of the proxy server on the network. The below table dictates the difference between a Port Number, IP Address, and Proxy Server Address. The below table gives you a glance at the difference between a port number, IP address, and proxy server address.
Comparison Table: Port Number vs IP Address vs Proxy Server Address
The below table gives you a glance at the difference between a port number, IP address, and proxy server address.
| Feature | Port Number | IP Address |
Proxy Server Address
|
| Purpose | Identifies a specific application or service on a device | Identifies a specific device on a network |
Masks the original IP address of a device
|
| Format | A number between 0 and 65535 | A unique numerical label assigned to each device on a network |
An IP address that acts as an intermediary
|
| Example | Port 80 for HTTP, Port 443 for HTTPS | 192.168.1.1, 255.255.255.0 | 192.0.2.1:8080 |
| Role in Networking | Directs incoming data to the correct application | Identifies the destination device for data packets |
Hides the original IP address, often used for privacy or security
|
What are the Different Types of Port Numbers?
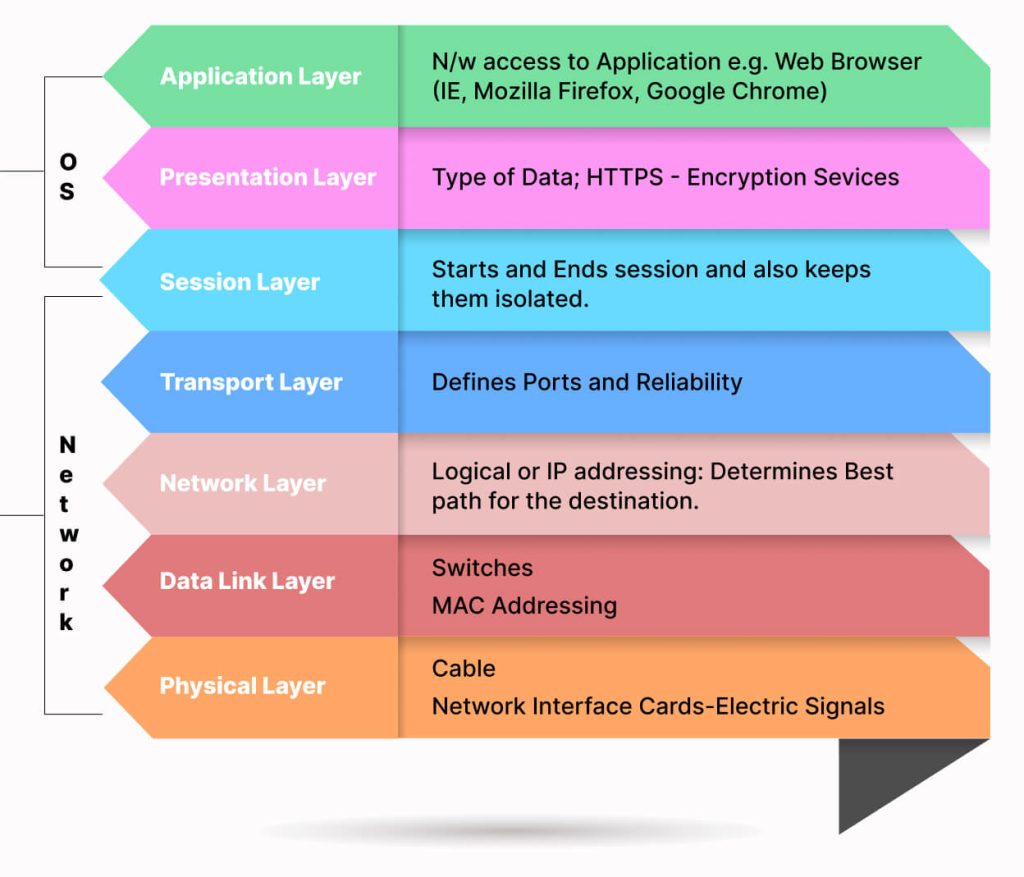
Logical ports are categorized into 3 main types which are:
- Well Known Ports
These port numbers range from 0 to 1023. Well-known port numbers are specifically reserved for standard services. For example, HyperText Transfer Protocol i.e. HTTP uses port 80, FTP uses port 21, DNS uses port 53, etc.
- Registered Ports
The range for these ports is from 1024 to 49151. Registered ports are assigned by the Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) to specific services and applications that are not very common.
- Dynamic Ports
Dynamic Ports are also called Private Ports or Ephemeral Ports. The range for these ports is 49152 to 65535. These ports are used for short-lived or temporary connections. Also, these ports are not pre-assigned to any specific service.
Now, we have learned about the different types of ports and the port ranges assigned to them. In the next section, let’s catch a glimpse of why these ports hold significant value in networking.
What are Some Commonly Used Ports?
There are a total of 65535 port numbers. So their range is from 0 to 65535. The list of port numbers is maintained by IANA and below are some commonly used port numbers along with their service and use. Have a look:
| Port Number | Protocol | Description |
| 21 | FTP |
File Transfer Protocol
|
| 22 | SSH | Secure Shell |
| 23 | Telnet |
Remote Terminal Access
|
| 25 | SMTP |
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
|
| 53 | DNS |
Domain Name System
|
| 80 | HTTP |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol
|
| 110 | POP3 |
Post Office Protocol 1 version 3
|
| 143 | IMAP |
Internet Message Access Protocol
|
| 443 | HTTPS 2 |
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
|
| 465 | SMTPS | SMTP Secure |
| 123 | NTP |
Network Time Protocol
|
| 5060 | SIP |
Session Initiation Protocol
|
| 16384-32767 | RTP |
Real-time Transport Protocol
|
| 2049 | NFS |
Network File System
|
| 3389 | RDP |
Remote Desktop Protocol
|
Importance of Ports
For effective communication and functioning of various services, ports serve as essential elements. Here’s how:
-
Differentiation of Services
If ports aren’t there, then it would be difficult to identify and differentiate various services and applications running on the same device. As each application and service is assigned a unique port number, multiple services and applications can run concurrently without any interference.
-
Efficient Routing of Data
Port numbers work in conjunction with IP addresses to direct incoming data to the appropriate service or application based on the assigned port number. Thus adding to the efficiency of the routing process.
-
Troubleshooting Network Issues
When diagnosing and troubleshooting network issues, it is important to understand which applications and services are involved. By understanding active port numbers, it becomes easy to figure out potential problems.
-
Quality of Service
Priorities can be assigned to various port numbers to manage different types of traffic. This way network admins can ensure that critical applications receive high bandwidth and thus perform better.
-
Standardized Communication
We know that every port number is assigned to a specific protocol or service. This enables standardized communication between applications on different platforms regardless of their underlying technology. For example, port 80 is used by HTTP, port 443 is used by HTTPS, and ports 20 and 21 are used by FTP.
-
Enhanced Security
Using firewalls, access to specific ports can be blocked through configuration. This selective filtering can help in blocking unauthorized access and thus enhance the security of the network. For example, port 22 when blocked prevents unauthorized remote login attempts.
-
Multiplexing Multiple Applications
It is because of ports that multiple applications can use the network simultaneously without any overlapping. Each application has its unique port number. The device uses this information to correctly route the incoming data to the intended application. Thus leaving no chance for confusion.
Practical Port Number Examples: Use Cases
There are endless applications and services in computer networking where ports are used. Some of the most common practical examples where ports are used:
- VoIP-SIP Communication
In VoIP-SIP Communication, i.e. making and receiving calls over the Internet, SIP protocol is used. The SIP protocol makes use of port number 5060 for the same.
- Remote Access
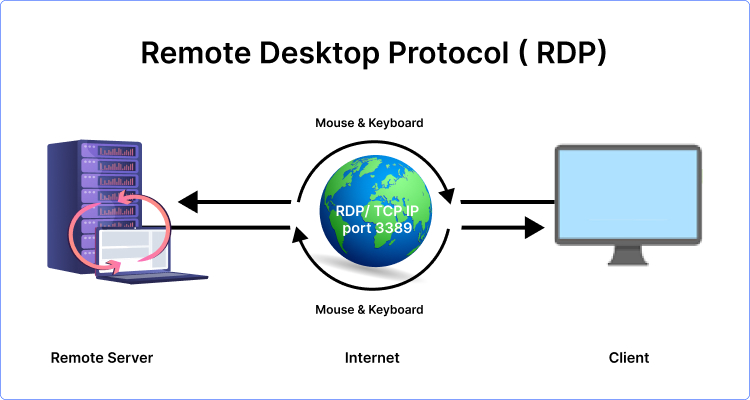
When a computer system is remotely accessed and controlled, the RDP i.e. Remote Desktop Protocol uses port 3389.
- Database Access
When accessing and querying databases, MySQL uses port 3306 and PostgreSQL uses port 5432.
How to Find Your Port Number?
There might be some instances when you need to find your port number. While I have explained everything about ports and port numbers, let’s take a look at how you can find your port number on your device.
How to Find Your Port Number on Windows
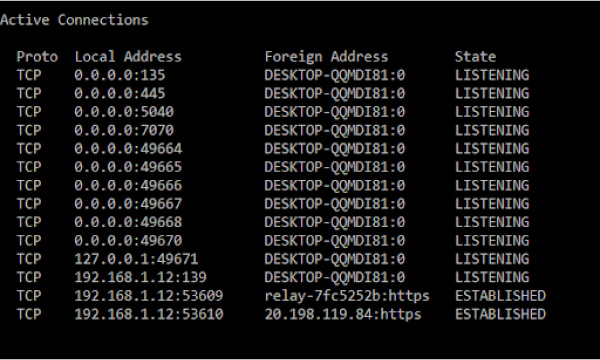
- First, type “Cmd” in the search box
- Now, open “Command Prompt”
- After that, enter the netstat -a command to see your port numbers
How to Find Your Port Number on Mac
- First, open “Terminal”
- Then, type the netstat -a | grep -i “listen” command and press “Enter” to see the list of opened ports
How to Open a Port on Windows 10 and 11
- First, go to the “Control Panel.”
- Now, go to “System and Security” -> “Windows Defender Firewall.”
- Then, select “Advanced settings.”
- Now, click on “Inbound Rules” on the left.
- After that, click on “New Rule” on the right.
- Then, select the “Port” option.
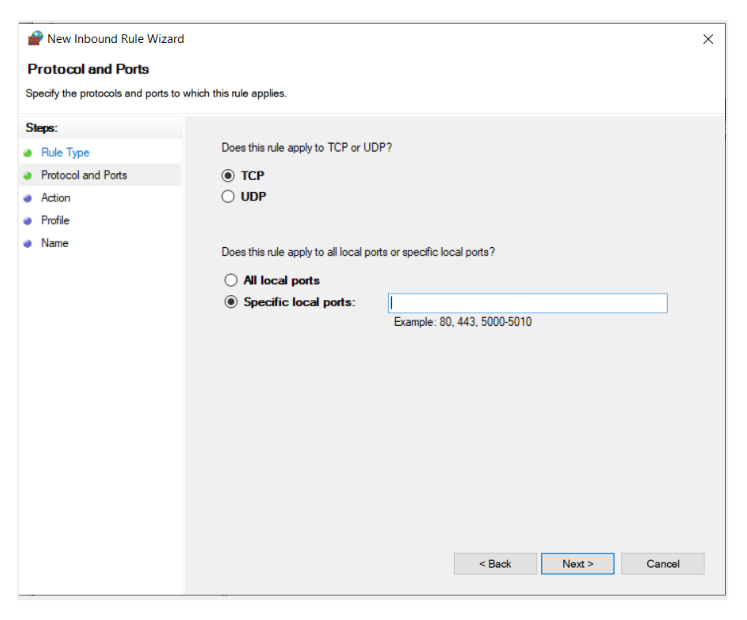
- Now, go to “Protocol and Ports.” Select the protocol (TCP or UDP) and add the port number to the “Specific Local Ports” section. If you want the list, then you can find the list here.
- In the next step, press “Next” and choose “Allow the connection.”
- Now, select what type of network this rule applies to and click “Next.”
- Then, add a name and short description to the rule and click “Finish.”
- At last, to close the port, simply remove the rule.
How to Open a Port on Mac?
- Start by opening “System Preferences.”
- Then, go to “Security and Privacy” > “Firewall” > “Firewall Options.”
- After that, tap the plus sign.
- Now, choose an application and click “Add.”
- Then, make sure that “Allow Incoming Connections” is turned on.
- Now, click “OK.”
- At last, to close the port, simply remove it from the list.
What is a Port Number? Key Takeaway!
From all that we have learned till now, it is clear that even the smallest details can have a significant impact on the grand architecture of the Internet. Ports and port numbers play a pivotal role in facilitating effective communication between devices and services. A proper understanding of port numbers is essential to configure firewalls, routers, and other network devices.
Happy Networking!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most popular ports on the internet?
Some of the most commonly used ports on the internet fall under the category of well-known ports. Have a look:
- Port 80 (HTTP): Used for unencrypted web traffic.
- Port 443 (HTTPS): Used for secure web traffic.
- Port 25 (SMTP): Used for sending emails.
- Port 21 (FTP): Used for file transfers.
- Port 22 (SSH): Used for secure shell access to remote devices.
- Port 53 (DNS): Used for domain name resolution.
- Port 110 (POP3): Used for receiving emails.
- Port 143 (IMAP): Used for managing email on a server.
Can multiple applications share the same port on a device?
No, ports are unique to every application or service that runs on a device at any given time. This means that multiple applications cannot share the same port on the same device simultaneously.
What happens when I try to connect to a closed port?
Usually, the connection will be dropped or refused by the device. This means that the port is not listening for incoming connections and the service you are trying to reach is unavailable on that port.
Can I modify the default port for a service?
Yes, it is possible to modify the default port for a service. For example, the default port for a web server is 80 for HTTP or 443 for HTTPS. You can configure the webserver to use a different port other than the default one. Most often, it is done for security reasons such as avoiding automated attacks. In such cases, you need to provide clients with the custom port number so that they can access your service.
What’s the difference between TCP and UDP ports?
The main difference between the two is how they handle data transmission. TCP i.e. Transmission Control Protocol is connection-oriented. This means that it establishes a connection first and then only transmits any data. In the case of UDP i.e. User Datagram Protocol, the data is sent without establishing a connection which means it is connectionless. TCP makes sure that accurate data is delivered in the correct order. While UDP offers no guarantee for the delivery and order of the data.
Why do Firewalls sometimes block specific ports?
This is done as a security measure to protect the network or device from getting compromised. Firewalls act as gatekeepers by blocking certain ports to prevent unauthorized access, provide protection against malware and DDoS attacks, and also control traffic to optimize network performance.
Note– This post has been updated on 09-12-2024.