Effective communication lies at the core of every successful business, and a dependable phone system serves as the foundation for smooth and seamless voice interactions within an organization. SIP and PRI are both telephony technologies that serve as vital tools for establishing communication channels in businesses. Comparing SIP vs PRI, we will learn that both technologies possess distinct characteristics that make them suitable for different organizational needs.
A few decades ago, PRI, often referred to as PRI trunking or PRI phone system, used to be the topmost choice for concurrent, high-speed communication. However, its popularity faded with time. These days businesses are increasingly turning to SIP trunking, a fully virtual, immensely scalable business phone system and communications solution.
Through this post, while we will understand both technologies in detail, first, let’s take a glance at the key differences between SIP trunking and PRI.
SIP vs PRI: Understanding the Core Differences
Traditional vs. Modern

PRI is a legacy technology that utilizes a physical wired connection (copper wires) and has a fixed capacity of up to 23 dedicated channels for voice calls.
SIP (Session Initiation Protocol) is the modern approach where the internet is used to transmit voice as data packets. In other words, communication happens over the Internet instead of traditional phone lines.
High-Cost vs. Cost-Effective

PRI typically comes with fixed monthly charges regardless of usage. It leads to a wastage of resources when a business experiences fluctuation in its call volume. Moreover, installation costs are also high due to the need for specialized equipment, dedicated lines, and professional setup by trained technicians.
SIP generally involves lower setup and maintenance costs because it offers pay-as-you-go flexibility. It often bills based on a ‘per-minute’ or ‘tiered’ calling plan that offers cost-effectiveness for businesses with variable call traffic.
Rigid vs. Scalable
PRI offers limited scalability as adding more capacity requires installing additional PRI lines. This is not only expensive but also time-consuming. Moreover, every new PRI line will always add exactly 23 new channels.
SIP is highly scalable as it offers ‘on-demand’ scalability. To add new SIP trunks or lines, users can simply adjust their service plan with the provider, choosing the one with a sufficient number of lines. This process of increasing and decreasing lines can be done online within a few minutes.
Basic vs. Advanced

PRI is limited to voice calls. If integration with other communication tools, like video conferencing, is needed, additional hardware or software installation may be necessary.
SIP integrates seamlessly with various IP-based business applications. Advanced features like call forwarding, video calling, and voicemail-to-email, are often readily available.
Low-Uptime vs. Highly Reliable
PRI is usually considered highly reliable because it has dedicated channels. However, vulnerabilities in physical infrastructure which is often on-site can disrupt the service.
SIP relies on the Internet. SIP providers often implement redundancy mechanisms and maintain geographically dispersed data centers to ensure continuity in service even during internet outages.
Now that we’ve quickly learned SIP vs PRI, let’s delve deeper into each technology to gain a more comprehensive understanding.
What is PRI and How Does it Work?
Primary Rate Interface or PRI is a telecommunications technology used to deliver multiple voice and data channels over a single physical line. It makes use of copper wires to digitally connect a business with a PSTN i.e. Public Switched Telephone Network.
Suppose a call is initiated from the customer’s PBX system. This PBX sends a signaling message to the telecom network via the D channel (Delta Channel) of the PRI. This message includes information about the call such as the caller’s number and the desired service i.e. voice call, data transfer, etc.
Based on the availability of resources and allocation policies, the telecom network allocates one or more B channels (Bearer Channels) for the call. Once channel allocation is done, the voice or data traffic starts transmitting between the caller and the called party over the assigned channels. When the call is completed and terminated, the allocated resources are released. It is then that the B channels are returned to the pool of available channels for future use.
Features of Primary Rate Interface (PRI)
Channelized Structure
PRI comes with a fixed number of channels, typically 23 B channels allowing for up to 23 concurrent voice calls, fax transmissions, or data sessions, and 1 D channel for call control information. This D channel handles tasks like call setup, routing, and signaling.
It is crucial to note that the B channels in PRI extend from 23 to 30 channels depending on the configuration.
Direct Inward Dialing (DID)
PRI supports Direct Inward Dialing or DID which enables businesses to assign individual phone numbers to employees without needing a separate physical line for each number. This allows direct external access to internal extensions without the need for operator assistance.
Compatibility
PRI integrates seamlessly with PBX systems which makes them a preferred choice for businesses with existing infrastructure. Since businesses already have PBX systems in place, integrating PRI can be a cost-effective solution compared to switching to entirely new communication technologies.
High Quality
PRI is a digital connection and offers superior call quality compared to analog lines. the voice transmission is clear and noise interference is minimal.
Pros and Cons of PRI
Advantages of PRI Trunking
High Capacity: A major benefit of PRI is that it offers high capacity for simultaneous voice calls and data transmissions. Typically it consists of 23 B (bearer) channels and 1 D (data) channel, which provides a total bandwidth of 1.544 Mbps in North America, and 30 B channels in Europe with a total bandwidth of 2.048 Mbps.
Reliability: PRI lines are quite popular for their reliability and stability. Because they are less susceptible to interference and noise when compared to analog lines, they offer better call quality.
Efficient Use of Resources: PRI efficiently utilizes bandwidth by dynamically allocating channels based on demand. This ensures optimal use of resources and cost-effectiveness.
Integration with PBX Systems: PRI facilitates seamless integration with Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems that are commonly used in businesses, enabling advanced call routing and management features.
Disadvantages of PRI
Cost: One of the key factors influencing technology adoption is cost and PRI implementation is often quite expensive due to initial setup. From purchasing the equipment as well as installation fees, the overall cost comes out to be high. This is a major hurdle for small businesses with limited budgets.
Limited Scalability: Another challenge with PRI trunking is its limited scalability. Scaling up PRI can be resource-consuming and costly. Adding additional channels or increasing capacity often requires hardware upgrades, which can involve significant time and expense. This lack of scalability may not suit businesses with fluctuating communication needs or those experiencing rapid growth.
Dependence on Physical Infrastructure: PRI trunks rely on physical infrastructure such as copper wires or fiber-optic cables. Any damage to this infrastructure, whether due to natural disasters, construction work, or vandalism, can lead to service disruptions. This can also make it difficult for businesses to quickly deploy or relocate PRI services.
Limited Flexibility: Compared to modern technologies like VoIP, PRI offers limited flexibility. PRI lines are tied to specific physical locations, making it challenging for remote employees to work from different locations or access communication services on the go. Additionally, PRI may not support features like softphones or mobile apps without additional integration.
Complex Configuration and Maintenance: Setting up and configuring PRI lines can be complex and require specialized technical expertise. Businesses need to hire skilled professionals for the maintenance and troubleshooting PRI infrastructure. This also increases operational overhead for businesses.
Single Point of Failure: Since PRI relies on a single physical connection to the telecommunications provider, it represents a single point of failure. Any issues with this connection can disrupt communication services for the entire organization until the problem is resolved. This lack of redundancy can pose a risk to business continuity and productivity.
What is SIP and How it Works?
SIP i.e. Session Initiation Protocol is a signaling protocol used for setting up, managing, and terminating real-time sessions involving voice and video, messaging, and other multimedia applications over the Internet. For easy understanding, you can consider SIP as a ‘conversation starter’ for your phone calls on the internet.
Working of SIP
Communication begins as SIP enables devices and applications to send SIP INVITE messages for initiating a session. To address participants in a communication session, SIP uses URIs i.e. Uniform Resource Identifiers, that usually have the format of a telephone number or SIP address.
Negotiation for various session parameters happens as the SIP messages are exchanged between the participants. This includes session duration, codecs, media types, etc. The routing of SIP messages between participants by proxy servers and redirect servers. Once the session is complete, SIP participants terminate the session by sending SIP messages indicating the end of the session.
What is SIP Trunking and How it Works?
SIP trunking is a service provided by ITSPs i.e. Internet Telephony Service Providers that leverages SIP protocol to enable businesses to make and receive voice calls over the Internet. SIP trunking connects a business’s PBX or Private Branch Exchange system to a PSTN or Public Switched Telephone Network via the Internet. SIP trunks are virtual trunks that replace physical phone lines with virtual ones.
To put it more simply, SIP trunking uses SIP protocol to establish communication sessions, typically for voice calls, over the Internet instead of traditional phone lines.
Here’s how SIP trunking works:
- The on-premise PBX system of the business, which acts as the central hub, is configured to communicate with the ITSP’s SIP trunking service.
- Once done, the connection establishment takes place as a user places a call from the PBX, which then sends a SIP request to the ITSP’s SIP trunking service over the internet.
- The ITSP’s SIP trunking service routes the call to the PSTN. once routed, the transmission of voice data between the caller and the recipient begins via the internet or PSTN.
- When the call is completed, signaling messages are sent by ITSP’s SIP trunking service. the call is terminated and resources are released which makes SIP trunks to be available for future calls.
Features of SIP Trunking
Saves Expenses
A Gartner analysis concluded that SIP trunks save companies up to 50% in telecom costs and significant savings from simplified billing strategies, which account for as much as 40% of total telecom spending. Source- AVOXI)
- With SIP trunking you enjoy cost benefits by leveraging the ‘pay-as-you-go’ model. Unlike traditional lines, SIP trunking providers allow you to pay only for the virtual trunks you use.
- As a business, you can enjoy reduced call rates, especially for long-distance calls since SIP trunking providers often offer competitive calling packages.
Offers Scalability and Flexibility
- You can easily scale your communication infrastructure up or down based on demand. Trunks can be added or removed within a fraction of a second to adapt to the changing needs without investing in additional hardware.
- SIP trunking supports remote communication thus helping businesses with distributed teams or multiple offices to enjoy geographical flexibility. With a centralized system, employees can connect to the corporate phone system regardless of their location.
Supports Advanced Features
- From call management features like voicemail, call forwarding, and conferencing, to auto attendants, SIP trunking supports a wide range of communication features.
- SIP trunking also supports unified communications, i.e. integrating voice, video, and instant messaging into a single platform allowing for seamless collaboration and productivity
High-Quality Voice Communication
The QoS feature of SIP trunking prioritizes voice traffic to ensure optimal call quality, even during network congestion.
Enhanced Security
SIP trunking providers implement various security measures like encryption, firewalls, and access controls to safeguard sensitive voice data and prevent interception of calls.
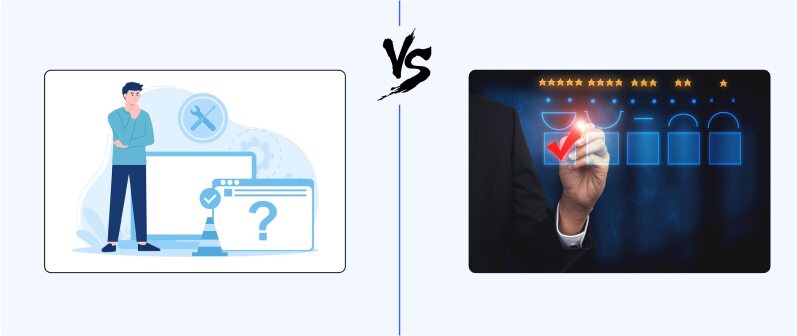
SIP Trunking Advantages and Disadvantages
Let’s look into the Advantages of SIP Trunking as well as its disadvantages:
SIP vs PRI: Which is the Best for Your Business?
Both PRI and SIP are technologies to make and receive calls, however, businesses must understand that the difference between SIP Trunk and PRI is that they cater to different needs.
When to Choose PRI?
-
Organizations with High Call Volume
PRI offers dedicated channels for simultaneous calls, which makes it best suited for businesses like call centers that experience a large number of inbound and outbound calls.
Example: An MNC with a large employee count and multiple geographically dispersed call centers can use PRI to ensure that they have a robust communication infrastructure in place to meet their organization’s communication needs.
-
Businesses with Legacy PBX Systems
PRI is also a preferred choice for businesses with existing PBX equipment. Since PRI integrates seamlessly with legacy hardware, it allows businesses to leverage their investment in existing infrastructure.
Example: A manufacturing business with an on-premise PBX system installed several years ago may opt for PRI to upgrade its telephony infrastructure while preserving its existing setup.
-
Industries Requiring Dedicated Lines

Many businesses require a reliable communication connection as they cannot afford downtime, PRI makes use of dedicated circuits making it suitable for such businesses.
Example: Hospitals handle emergency calls which is why they need a reliable phone system technology just like the PRI phone system.
When to Choose SIP?
-
Cost-Conscious Businesses

Due to its cost-effectiveness (competitive rates for long-distance calls and pay-as-you-go model), SIP is an excellent choice for small to medium-sized businesses that seek affordable yet effective business phone solutions.
Example: A startup business with a remote workforce can enable its employees to connect over long-distance calls without incurring high international call charges.
-
Businesses with Dynamic Communication Needs
Companies that experience fluctuating call volumes or seasonal variations often seek a solution like SIP trunking that allows easy addition and removal of channels.
Example: A retail business experiences a sudden increase in call traffic during the holiday season. Using SIP trunking, such a business can quickly add additional virtual trunk lines to handle the increased call volume and remove those lines once the busy season is over.
-
Companies with Remote Teams
 SIP trunking is a great option for businesses with remote workers and multiple offices. Such businesses need a centralized call management solution so that their employees can connect no matter where they are and SIP suffices the same.
SIP trunking is a great option for businesses with remote workers and multiple offices. Such businesses need a centralized call management solution so that their employees can connect no matter where they are and SIP suffices the same.
Example: A consulting firm with offices across the globe can use SIP trunking to have a single phone system with local phone numbers for each location.
PRI Line vs SIP Trunk: Wrapping Up!
Statistics reveal that “Over 90% of businesses rely on phone systems as the main communication tool.” Business phone systems define the success of business communication, but it’s the underlying technologies that carry greater significance.
In this post, I have explored SIP Trunking vs PRI. PRI relies on dedicated lines to facilitate voice transmission, while SIP trunking utilizes virtual lines to manage voice and data transmissions. each approach has its advantages and disadvantages.
While PRI is a longstanding technology in telecom, SIP adoption has been on a rapid increase owing to the wide range of benefits offered by it. SIP trunking is a cost-effective and scalable solution offering easy management and flexibility for growth. On the other hand, PRI remains a solid choice for businesses with stringent requirements.
When choosing your communication champion between PRI and SIP trunking, it’s important to assess your specific requirements and carefully weigh the pros and cons of each option.