The Internet has seamlessly woven itself into our daily lives. However, numerous companies around the world persist with outdated telephony systems. Reason? Probably they are unable to make an immediate leap to VoIP. But then, the question arises: how can they still tap into VoIP advantages? This is where a VoIP gateway comes in. These gateways connect your old-school phones with the internet era. Before we move into the details, let’s give you a quick headshot about the VoIP technology statistics and reveal its transformative influence.
Did you know “About 31% of businesses use VoIP systems in their daily workflows.” and “The VoIP market size will grow to $102.5 billion worldwide by 2026.”
Of course, the figures are impressive. Now let’s proceed with this informative blog. Here we are going to give you a detailed understanding of VoIP gateways, how VoIP gateways work, their setup, some of the best VoIP gateway manufacturers, and a lot more.
Come join in!
What is a VoIP Gateway?
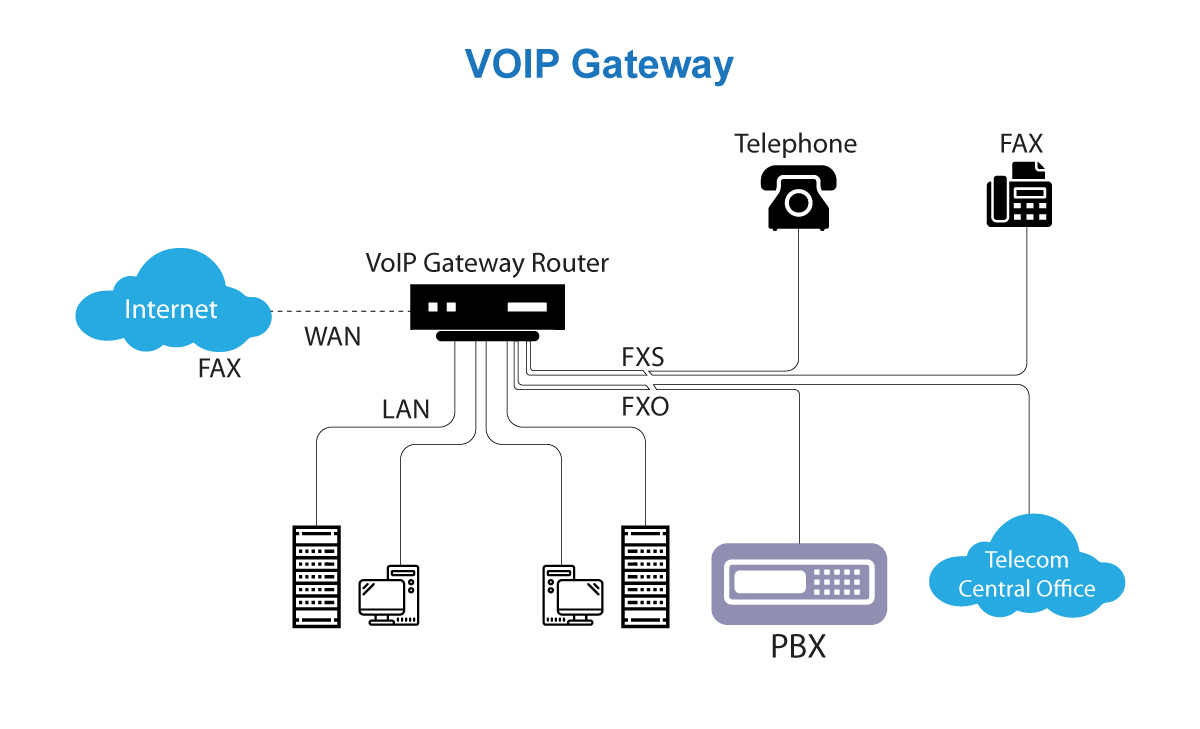
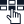
Voice over Internet Protocol Gateway is a physical device or a software application that converts analog telephony traffic into digital data packets and vice-versa for seamless transmission over the Internet. Without a VoIP gateway, signals from one system would not be able to transmit to the other due to incompatibility between them. This mismatch would result in signals getting trapped while making attempts to transition between the two systems.
In simple words, a VoIP gateway acts like a bridge between your traditional phone system and the modern Internet world. It converts regular phone calls into internet-friendly messages. So you can make calls over the Internet using your regular landline phone.
How Does VoIP Gateway Work?
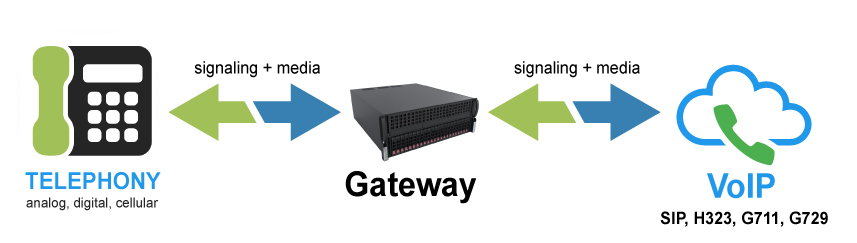
Analog to Digital Conversion
When a call is initiated from the PSTN, the VoIP gateway receives the analog signal and converts it into digital data. Then it performs Compression using codecs to break down this digital signal into small data packets. These packets contain information about the call such as voice data and routing details. This series of tiny data packets are transferred across the Internet Protocol network. Upon reaching the recipient’s VoIP gateway of the endpoint, the gateway converts digital data back into an analog signal. This conversion allows the traditional phone to understand the message and thus the recipient hears the voice message.
From IP Network
In the case where the call originates from an IP network, the VoIP gateways work in reverse order which is completely different from when the signal originates from traditional phones. Firstly, the digital data packets are decompressed into digital signals. Then these signals are converted into analog signals to be sent across PSTN.
VoIP Protocols and Codecs
As we discuss VoIP gateways, we must know about protocols and codecs used in VoIP. This is because protocols and codecs are vital components of VoIP functioning. Let’s understand:
VoIP Protocols

These are a set of rules or standards that determine how voice and other multimedia content will flow over the internet. A VoIP gateway typically supports one protocol. Some of the most widely used VoIP protocols are:
- SIP
- RTP
- MGCP
- H.323
VoIP Codecs
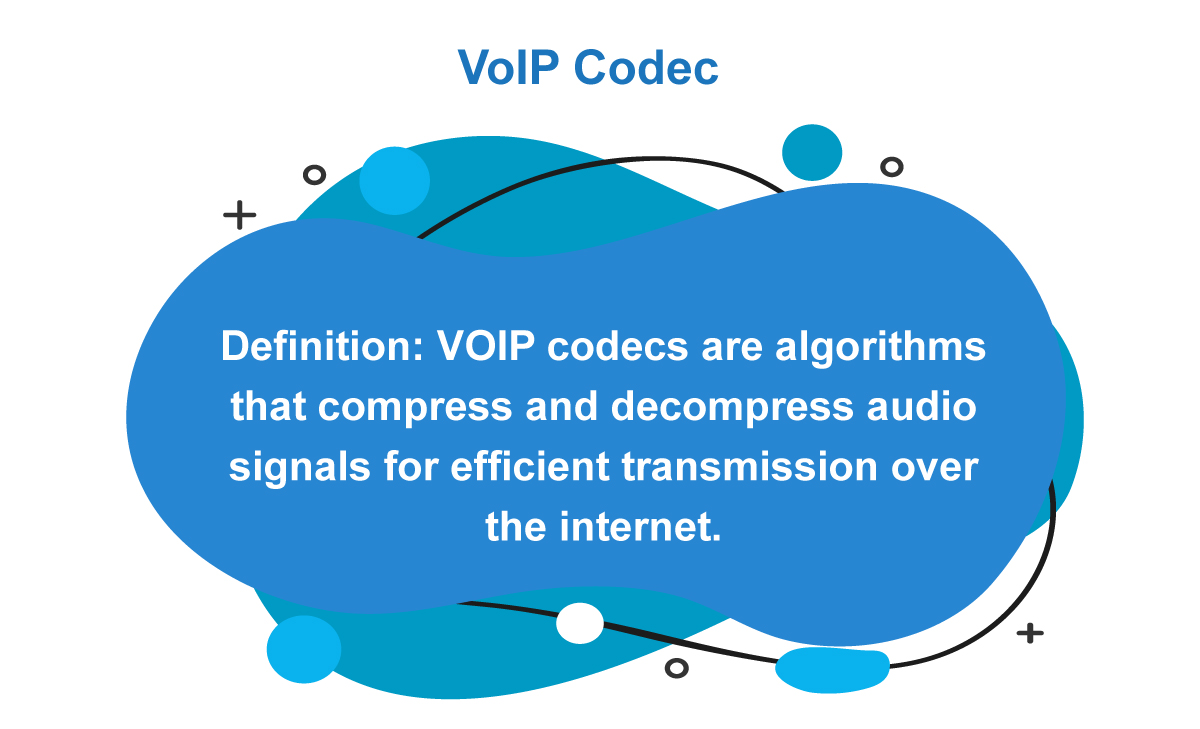
These are algorithms that compress and decompress a voice stream for transmission over the internet. Codecs also play a crucial role in determining the quality and bandwidth requirements for packets to be sent across. Some of the most common VoIP codecs are:
- GSM
- iLBC
- G.711
- G.722
- G.726
- G.728
- G.729
Types of VoIP Gateways
What is VoIP gateway used for? The answer to this question lies in the type of VoIP gateways. They come in various forms depending upon the purpose they serve.
Analog VoIP Gateway
Analog VoIP gateways are used to connect traditional analog phones such as regular landline telephones and fax machines to a VoIP network. It also works vice-versa i.e. connect your VoIP phone system to the PSTN. Due to this dual functionality and purpose, analog VoIP gateways come in two different forms:
FXO: Foreign Exchange Office is an interface that connects your VoIP phone system to PSTN lines. Here’s a simple example – Suppose there’s a small business that uses VoIP communication but still needs to connect with a standard telephone service provided by a local telecom company. Here, the FXO acts as a gateway that enables the VoIP system to connect with the outside world and utilize the services provided by the telecom provider.
FXS: Foreign Exchange Subscriber or FXS is an interface that connects analog devices to a VoIP system. To understand the role of FXS, consider the scenario of the same small business mentioned above. The FXS interface allows the analog devices within the same small office to connect and function within the VoIP network.
Digital VoIP Gateway
Digital VoIP gateways convert digital signals from one type of protocol or network to another to ensure smooth communication. They connect digital lines typically with:
- ISDN Lines: Integrated Service Digital Network (ISDN) Lines supports simultaneous digital data transmission over the traditional PSTN or other digital lines.
- T1 Lines: These are high-speed communication lines that can carry multiple voice or data channels. These lines are primarily used in the North American region.
- E1 Lines: These are also high-speed communication lines like the T1 lines but used outside North America. E1 lines are mostly used in Europe and other parts of the world.
- PRI i.e. Primary Rate Interface: Often used for connecting to the PSTN, PRI is an interface that provides multiple channels for transmission of voice and data.
Hybrid VoIP Gateway
As the term suggests, the hybrid VoIP Gateways combines functionalities from both analog and digital VoIP gateways. It acts as a versatile tool by converting both analog and digital signals at the same time. Thus, enabling the concurrent use of different types of devices and networks within a VoIP environment.
Session Border Controller (SBC)
SBCs are powerful VoIP gateways that perform a critical role in signaling and transfer of data in real-time communication such as VoIP calls. SBCs perform various tasks like encryption, call routing, quality of service, and protocol translation. With this, it ensures secure and seamless communication between different types of networks.
Enterprise Session Border Controller (E-SBC)
A popular type of Session Border Controller, E-SBCs are designed specifically for large-scale deployments. E-SBCs are installed at the edge of an enterprise or corporate IP network. By managing and securing communication sessions, E-SBCs maintain the quality and integrity of communication across the enterprise.
Features of VoIP Gateways
VoIP Gateways come with various features to facilitate smooth communication across different devices and networks. Here are some of the most common features:
- Call Routing
VoIP gateways manage call routing between different networks. They implement Least Cost Routing i.e. LCR to choose the most cost-effective path towards the destination.
- Packetization
VoIP gateways play a crucial role in the packetization and de-packetization of voice signals. As explained before, during packetization, the voice signals are broken down into smaller packets for transmission over IP networks. During depacketization, these packets are converted back to analog signals for compatibility with traditional phone systems.
- Protocol Conversion
VoIP Gateways enable compatibility between various networks by translating between different protocols. They are compliant with multiple protocols including SIP, H.323 and MGCP
- Codec Support
Voice signals need to be converted and transmitted into different formats for optimal call quality. VoIP Gateways support various audio codecs such as G.711, G.723.1, G.726, and G.729A voice codecs to ensure the same.
- Voice and Fax Integration
Many VoIP Gateways support voice communication and fax and data transmission over IP networks. They convert voice or fax signals into data packets thus allowing users to make/send and receive voice calls and faxes. Such capability is extremely useful for businesses that rely on voice and fax communication.
Benefits of VoIP Gateways
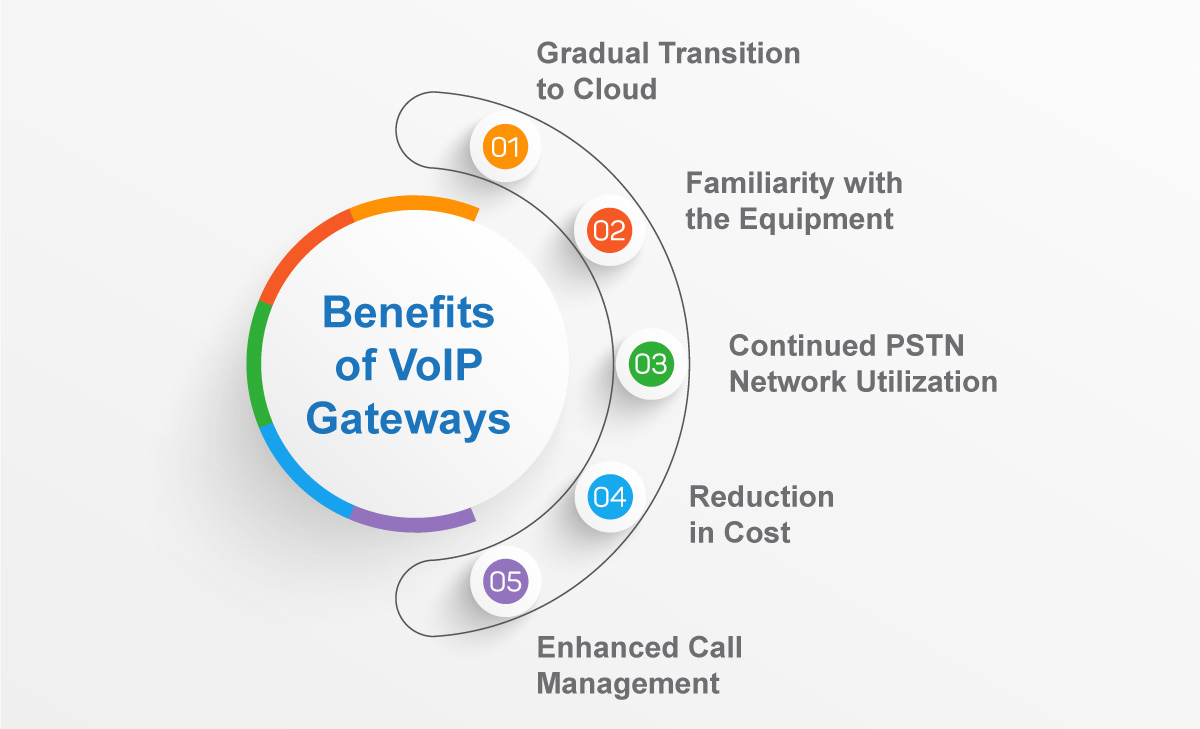
Gradual Transition to Cloud
With VoIP Gateways, businesses can gradually transition to cloud-based communication systems. VoIP gateways help in connecting analog phones or PBX systems with the cloud infrastructure. By retaining their existing hardware companies can stagger the cost of migration. So there is no overwhelming expenditure on infrastructure, allowing businesses to transition at their own pace.
Familiarity with the Equipment
Using VoIP gateways, businesses can continue to use their existing devices. These gateways act as bridges, enabling devices such as analog phones to function seamlessly within a modern VoIP environment. The business can invest its resources in something other than extensive staff training or introducing an entirely new communication system.
Continued PSTN Network Utilization
We know that VoIP gateways enable communication between the PSTN i.e. Public Switched Telephone Network and VoIP networks. They enable users to enjoy the benefits of VoIP technology while still making and receiving calls from the PSTN.
Reduction in Cost
Using VoIP Gateways, companies can connect to cloud-based UCaaS services without investing in expensive hardware such as desk phones. It lets users take advantage of modern telephony and enjoy calling through software applications.
Enhanced Call Management
VoIP gateways connect your old technology with the new. Traditional telephony only converts one call at a time. However, with VoIP gateways, you can receive multiple calls simultaneously. This expands your call capacity and thus improves customer service.
6 Easy Steps to Set Up VoIP Gateway

While the specific steps to set up a VoIP gateway will vary from one system to the other, we are going to explain some common yet useful steps that are quite similar across various VoIP gateway solutions.
1. Select the VoIP Gateway
To set up a VoIP gateway you will need one considering various factors such as your business requirements, number of analog devices you would like to connect, features, etc. We will discuss this in detail later in this blog.
2. Connectivity and Hardware Setup

Start by connecting your VoIP gateway to your network infrastructure. You will be required to use Ethernet cables to make these connections.
Figure out the analog devices such as your landline phones and fax machines. Connect these devices to the VoIP gateway through appropriate ports on the gateway.
3. Access the VoIP Gateway Interface
Open your web browser to access the VoIP gateway’s admin interface. You can do this by entering the gateway’s IP address on your browser’s address bar.
A login screen will appear. Enter the credentials i.e. username and password provided by your gateway vendor.
4. Perform Configuration
Start with basic network settings. You can configure the IP address, subnet mask, and address of the gateway.
Then you can set up the call routing rules. These rules will define how incoming and outgoing calls will be handled.
Expert Tip: When setting up a VoIP gateway, ensure your network prioritizes Quality of Service (QoS) settings to guarantee stable bandwidth for voice traffic, reducing latency and ensuring clearer communication.
5. Testing and Troubleshooting
Once done with the configuration, it’s time to test the setup. Start by making simple calls. Check whether connectivity and functionality are working fine.
If any issues arise, you can troubleshoot or get assistance from your VoIP gateway provider.
6. Security Considerations
Make sure to set up strong passwords and apply the latest firmware updates to stay protected against vulnerabilities.
VoIP Gateway: Use Cases
SMBs
VoIP gateways are an excellent opportunity for small to medium-sized businesses to leverage advanced communication features and functionalities. Using VoIP Gateways, small businesses can transition from traditional telephone systems to VoIP budget-friendly VoIP solutions.
Telecom Service Providers

Service providers in the telecom industry use VoIP gateways as a crucial element to interconnect diverse networks. Suppose, a telecom service provider wants to offer VoIP services while still maintaining connectivity with traditional telephony. The provider will deploy VoIP gateways to convert calls between PSTN and VoIP.
Factors to Consider when Choosing a VoIP Gateway
An enterprise like yours must take into consideration the following factors when selecting a VoIP Gateway that’s the right fit:
Cost and Budget
The cost of VoIP gateways can vary significantly from one vendor to another. It is better to consider upfront expenses and ongoing operational costs. Along with the cost of hardware, you must also include licensing fees, maintenance, and support expenses.
Call Load
The VoIP Gateway you select must accommodate your current VoIP voice call capacity and must also allow for future expansion without any significant investment or changes. Get an estimate of the volume of calls your business receives in a day, especially during peak hours. Now increase that number by at least 25 to 30% for future growth.
Consider conducting a thorough cost analysis based on your expected call volume. For instance, if you estimate an average of 100 concurrent calls, calculate the gateway’s capacity requirements and associated licensing costs, ensuring scalability to, say, 150-200 calls to accommodate future growth without immediately incurring additional expenses. This approach helps optimize initial investment while preparing for expansion.
Compatibility and Connectivity
What if you choose a VoIP gateway that does not work in alignment with your existing infrastructure? The VoIP Gateway you choose must support the necessary protocols. Some of the most commonly used protocols are SIP and H.323. In terms of interfaces, the VoIP gateway must also support FXO, FXS, and PRI interfaces for proper functioning.
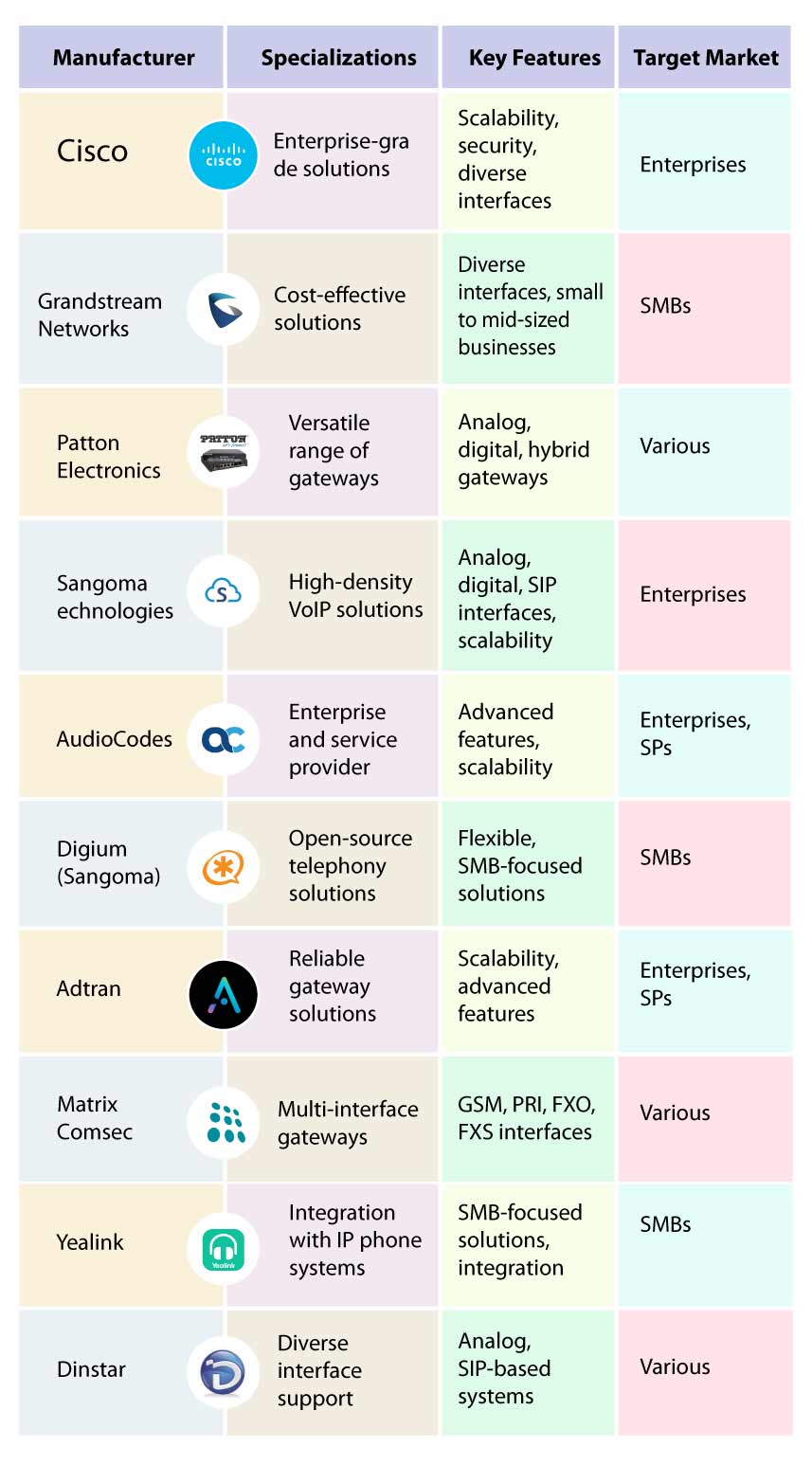
Top 10 VoIP Gateway Manufacturers
Conclusion
As we conclude, we embrace the words of renowned industry sage, John Doe,
‘The gateway to unparalleled communication lies in VoIP’s transformative power.’
VoIP gateways are truly the architects of a connected tomorrow, transforming the way we connect, converse, and create. We hope that this blog provided you with useful insights about what is a VoIP gateway. If you need any type of assistance regarding VoIP from our industry experts, please get in touch with us today!