“We are all now connected by the Internet, like neurons in a giant brain.” is a wise statement by Stephen Hawkings. It’s amazing that more than 5.3 billion people around the globe are connected to the internet. But who connects us to the internet and ensures a smooth online experience every single time? Well, it’s ISPs, or Internet Service Providers, also called Internet Providers or Network Providers. Through this blog, we will learn what an ISP is, what they do, how an ISP works, and most importantly, the types of services they offer. By the end of this blog, you will also learn about the exact steps to start an ISP business.
Let’s dive in!
What is an ISP or Internet Service Provider?
An ISP, or Internet Service Provider, is a company or organization that provides internet access to individual and business customers. ISP companies are organized in different forms, such as privately owned, community-owned, non-profit, and commercial. People who subscribe to the services of an ISP pay a nominal fee to enjoy online services like playing video games, using social media, shopping from e-commerce stores, managing business-related activities, and a lot more.
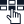
Here’s an example for you to understand the role of ISPs.
Imagine: It’s weekend time, and to set up the vibe, you plan to enjoy a movie night at home. With the flick of a button, you effortlessly power up your smart TV. Navigating through the latest movie options, you find the one that piques your interest. All your online activities are effortless and enjoyable, thanks to the reliable internet connectivity provided by ISPs.
Is an ISP the Same As the WiFi Provider?
Often ISPs are confused with WiFi providers, but they are different. ISPs deliver internet services through broadband, satellite, or wireless channels. They provide the infrastructure and services that enable users to get internet access.
On the other hand, WiFi providers offer wireless internet connectivity to users within a specified local network. The simplest example of a WiFi service is the public WiFi hotspots and even the private WiFi networks in homes. In layman’s language, we can say that ISPs provide broader internet services, while WiFi providers focus specifically on wireless connectivity.
Can You Connect with the Internet Without an ISP?
The precise answer will be no; however, I’ll explain that as well. Whether you are a home user or an organization, your ISP is the entity that provides you with the necessary infrastructure to connect with the vast internet out there. In other words, an ISP is an intermediary that links your device with the broader internet.
While there are alternatives, such as a cellular service or a LAN, to connect devices to the internet, they do come with limitations. All in all, an ISP remains the primary means to access the internet.
How Do I Find My ISP?
There are several occasions when you might need to find your ISP. You may encounter issues with your internet connection and want to connect with your ISP to get help. You may detect suspicious network activity or have some security concerns, which makes it important to know your ISP. Also, for billing or account-related queries, you may need to contact your ISP directly.
So if you are unsure and want to find your ISP, then here are some easy ways for you:
Check Your Router
The router or modem that you use for internet connectivity usually has the name of the ISP displayed on them. You may check the labels on the device to find this information.
Review Your Internet Bill
One of the easiest ways to find who your ISP is. Whether you get the bill in paper form or an email statement, you can easily find the name of the ISP listed on that.
Use Online Services
There are various websites and tools that can help you identify your ISP. These services make use of your IP address to track your Internet Service Provider. You can simply search Google for “find my ISP,” and it will show you the relevant results.
Check Network Settings on Your Device
You can also find your ISP by checking the network settings on your device, such as a laptop.
For Windows and Mac, you may go like this:
- Windows
Go to Control Panel > Network and Sharing Center > Connections, then check your active internet connection.
- Mac
Go to System Preferences > Network, and check the details of your connection.
Evolution of ISPs
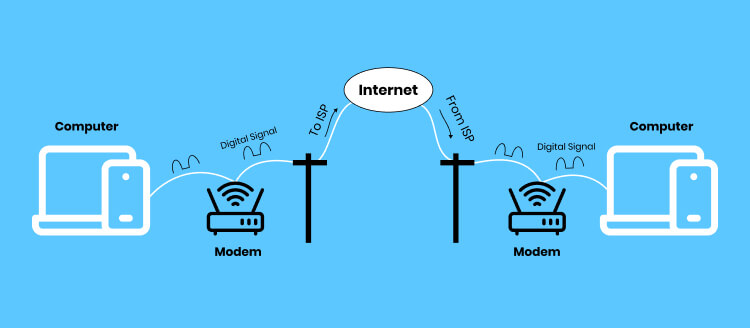
Access to the Internet began with dial-up connections. At that time, users used to connect their computer devices with a telephone line and a modem to get access to the Internet. Not only the data transfer rates were slow, usually around 56 kbps, but often the connection was unreliable too.
Then happened the Broadband Revolution, where ISPs began offering DSL, cable, and fiber internet services. The data transfer speeds improved significantly, usually around 1 Mbps. After this, came wireless technologies like WiFi and cellular, which gave rise to mobile ISPs for internet connectivity while on the go.
Then the fiber optic expansion took place, through which users could access the internet at ultra-fast speeds (gigabit). Besides fiber optics, new technologies like satellite internet for rural and remote areas emerged as an alternative. Since then, there has been no looking back, and today we are witnessing services like 5G internet that offer peak speeds of 10 Gbps along with reliability and better capacity.
What is the Purpose of ISP?
We have already learned that ISPs facilitate internet access for users worldwide. However, besides this, ISPs offer some advantageous benefits to individuals and businesses, which we are going to discuss below:
Essential Connectivity
Global connectivity is one of the most significant advantages offered by ISPs. Through the Internet, a small business in a rural area can connect with customers across the globe. Remote collaboration is another major benefit offered by ISPs. Employees can connect just from anywhere and collaborate seamlessly with their teams.
Variety of Options
No matter if you need internet access for business use or personal entertainment, your requirements are unique from others. ISPs provide a wide variety of options for internet connections, such as DSL, cable, fiber optic, satellite, etc. Furthermore, ISPs also offer a variety of data plans and speeds to cater to different requirements of their customers. You can easily choose a plan according to your budget, usage level, and type.
Reliable Services
Reputable internet service providers ensure an excellent customer experience by offering high uptime and performance. They have automatic failover systems that can reroute traffic if one server goes down to ensure consistent internet access.
What are the Different Types of ISPs?
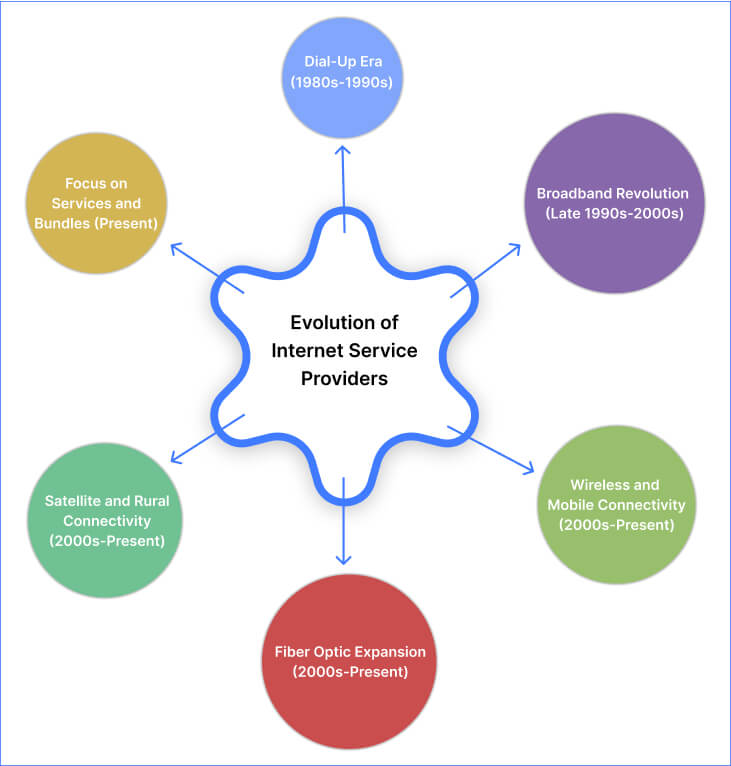
In the global internet hierarchy, ISPs are classified mainly into three categories as mentioned below:
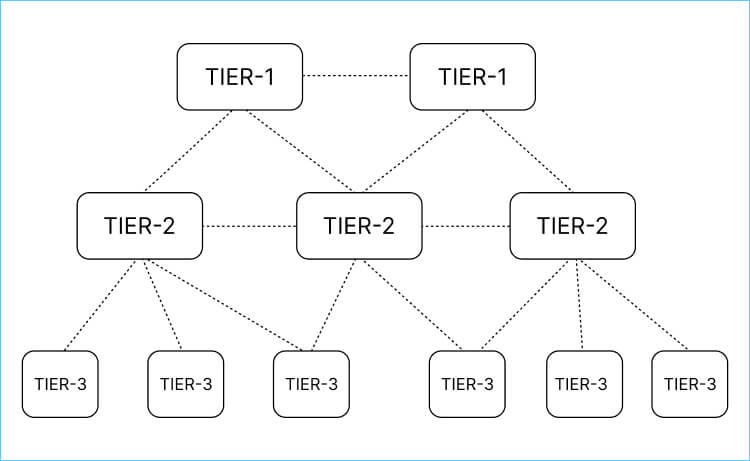
Tier 1 ISPs
They come at the top level, having extensive global reach covering multiple regions and continents. They have enough physical network lines or peer directly with other Tier 1 ISPs to exchange traffic freely. Tier 1 ISPs invest heavily in setting up the infrastructure.
Tier 2 ISPs
Tier 2 ISPs operate within regional networks and connect with Tier 1 ISPs to access the broader internet. This also means that Tier 1 ISPs sell their network access to Tier 2 ISPs. Other than this, Tier 2 ISPs may also partner with their counterparts, i.e., other Tier 2 ISPs, for bandwidth exchange. These ISPs focus mainly on commercial and end users like homes, businesses, and individuals.
Tier 3 ISPs
The last category is Tier 3 ISPs, which are responsible for connecting customers to the internet by peering agreements with higher-tier ISPs. Their focus is mainly on end users.
Besides the tier-based hierarchy, ISPs are also solely classified based on the geographic scope of their operations. Let’s have a look:
Local ISPs
These ISPs have limited service areas, i.e., they provide internet connectivity to single locations. Their size and scale depend upon the defined geographic area. Their customer base usually consists of corporates and consumers within those particular localities.
Regional ISPs
They serve more than one locality and have a customer base of more than 10K. Often local and regional ISPs are considered the same, but there’s a little difference. For example, within a large state, an ISP serving multiple cities will be considered a regional ISP, and an ISP serving only one city will be a local ISP.
National ISPs
A national ISP provides internet connectivity on a broader scale, which could be an entire nation. They have heavy infrastructure and the capabilities to meet customer demands spanning multiple regions and states. In comparison to local ISPs, national ISPs offer relatively higher-speed connections. National ISPs are a good choice for companies that operate in several locations and have on-the-go employees.
Types of Internet Connections Offered By ISPs
Below mentioned are the different technologies through which ISPs deliver their services:
Broadband Service
It is high-speed internet access that transmits large amounts of data at high speeds. Broadband service can be delivered through DSL, fiber optic, cable modem, satellite, and wireless.
Digital Subscriber Line
In this type of internet connection, existing copper telephone lines are used to transmit digital data. DSL connections are usually faster than dial-up connections but slower than fiber optic internet.
Fiber Optic
the fiber optic internet makes use of thin strands of glass or plastic fiber to transmit data as pulses of light. the speed offered by this type of connection is usually high.
Wireless Internet
Also called WiFi, the wireless internet connection allows internet access to users without using physical cables. It makes use of wireless routers and radio signals for the transmission of data. Today, wireless internet is widely popular in residential and commercial sectors.
Satellite Internet
Often used in remote areas, Satellite internet delivers internet access by sending and receiving signals between satellite dishes installed at the user’s location and in the geostationary orbit above Earth. Compared to other internet connections, satellite internet can have higher latency and slower speeds.
How Does ISP Work?
Now we know that ISPs act as middlemen between you and the vast space of the Internet. But how does an ISP provide Internet? Here it is:
Network Infrastructure
ISPs maintain their own network infrastructure which includes various technologies like fiber optics, DSL, satellite links, or wireless connections. This infrastructure enables ISPs to connect with a global network called as Internet backbone. This is a high-capacity network where various ISPs and network providers are interconnected.
Obtaining IP Addresses
Internet service providers acquire blocks of IP addresses which they assign to their customers. These addresses allow data to be directed to the right destinations.
Providing Internet Access to Customers
Now as you, the customers, subscribe to the services of an ISP, it provides you with an internet connection based on your preferences in terms of speed, availability, etc. The ISP then assigns you an IP address which is your unique identifier on the internet.
Routing Your Traffic
When you type in a web address or click a link, your request travels through your ISP’s network. Here data is transmitted in the form of packets and ISP routers and switches transmit these packets to their intended destination. This process involves finding the best routing path for the data to reach its destination.
Delivery of Content
Once your request reaches the destination server, the requested information is sent back the same way which is ultimately received by your device.
How to Choose an ISP?
Residential customers and businesses often get overwhelmed with the availability of various ISPs. Here are some important factors to consider when choosing the right ISP.
Location
Different ISPs have different coverage areas. So you have to check and find the ones that serve in your area. Usually, there are fewer options if you are in a rural or remote region. On the other hand, users in urban areas may find more options.
Speed
What is the speed that you require for your online activities? Simple browsing and surfing may not require fast internet connectivity. While streaming videos and online gaming require more speed and bandwidth. Even those working from home usually require more speed to upload large files and make video calls. Here’s a table highlighting the speeds required for different types of online activities:
| Activity | Recommended Bandwidth |
| Web browsing | 512 Kbps or less |
| 128 Kbps | |
| Basic online shopping | 256 Kbps to 512 Kbps |
| Streaming standard-definition video | 1 Mbps to 3 Mbps |
| Online gaming (casual games) | 2 Mbps to 5 Mbps |
| Downloading music | 512 Kbps to 1 Mbps |
| Streaming high-definition video (HD) | 5 Mbps to 10 Mbps |
| Online gaming (high-end games) | 10 Mbps or more |
| Video conferencing (with multiple participants) | 5 Mbps to 10 Mbps |
| Downloading large files (e.g., movies, software) | 10 Mbps or more |
| VoIP calling | 100 Kbps (minimum), 256 Kbps (recommended) |
Budget
Depending upon your specific requirements, you will have to pay for the internet connectivity. For basic browsing and emailing, the cost of the connection will be less. For faster speeds, you will need to pay more. Many ISPs offer bundled services such as TV, phone, and internet. You can go for such options if you find them beneficial. Also, check about data caps and equipment costs to have an estimate about the overall cost of the connection.
What Information Can ISP See?
The information visible to ISPs usually includes your browsing history, IP addresses, DNS requests, Device Information, Connection Timestamps, Data Usage, and type of Traffic.
How to Start an Internet Service Provider Business?
Probably, the reason why you are reading this article is that you have been thinking about starting an internet service provider business. Though the market is already crowded, that doesn’t mean that new players cannot stand out. Trust me, the demand in this market is growing like never before which makes way for huge opportunities to get success.
With that in mind, let’s take a look at the criteria for how to start an internet service provider business. Here is a solid plan consisting of 9 important steps to quickly turn your idea of becoming an ISP into reality.
Your 9-Step Roadmap to ISP Business
1. Do the Evaluation
Several aspects need to be evaluated. These include the following:
- Identify Your Target Area
Choose an underserved area with limited and unreliable access to the Internet.
- Determine Your Target Customer
Define your target customers based on age and gender.
- Determine the size of your Audience
Assess the population density in the target area to have an idea about your potential customer base.
- Analyze the Competition
Research the market and figure out your competitors or existing providers. Check and understand their service offerings. Some of the most popular and well-established names in the Internet Service Provider industry are AT&T, Cox Communications, Verizon, and many more. The below table lists the same:
Examples of Internet Service Providers
| ISP Name | Description |
| AT&T | The largest U.S. telecom company with extensive fiber and mobile networks. |
| Comcast | Leading cable and internet provider in the U.S., known for the Xfinity brand. |
| Verizon | Major wireless and internet provider, offering FiOS fiber service in select areas. |
| Charter Spectrum | Second-largest cable operator in the U.S., serving mainly in the Midwest and Southeast. |
| Cox Communications | Third-largest cable operator in the U.S., focusing on the West Coast and Southwest. |
| Deutsche Telekom | Dominant telecom provider in Germany and Europe, offering a range of internet services. |
| China Telecom | The largest fixed-line telecommunications provider in China, with extensive network coverage. |
| Orange | Leading telecom company in France and Africa, offering mobile, broadband, and TV services. |
| NTT Group | The largest telecom and IT company in Japan, providing internet, mobile, and cloud services. |
| Telefonica | Spanish multinational telecom company with operations in Europe and Latin America. |
2. Get a Comprehensive Business Plan
Creating a business plan doesn’t guarantee your chances of success but it gives you a roadmap to stay focused and organized. Also, by outlining a plan you will be able to identify any potential issues that may arise later. Such a plan provides a clear vision for the future of business and can be your foundation to make the right decisions To create a good business plan for your internet service provider business, consider adding the following essential elements:
- What are your goals?
- Estimated amount of money you’ll need to start the business
- The number of employees you’ll need to hire
- How you will provide service to customers?
- How much will you charge for your services?
- How you will deal with problems like maintenance issues?
If you are still not sure how to generate a business plan, then there are many business plan generating services available online. You can try a few and see if it works up to your expectations.
Bonus Tip: You can explore traditional bank loans and angel investors for your funding needs. Also, don’t forget to check government grants or subsidies provided to ISPs serving in underserved areas.
3. Decide Upon a Suitable Business Structure
There are various options to choose from when it comes to “how you want to operate?” These are
- Sole Proprietorship: You are the boss – all profits and debts are yours.
- Partnership: Run by 2 or more people, share profits and debts based on agreement.
- LLC: Combines the liability protection of a corporation with the tax flexibility of a partnership.
- Corporation: Separate legal entity, owners not personally liable, subject to double taxation.
You can research each of these structures to figure out which one makes the most sense to you. Also, each structure comes with its own legalities, so it is a good idea to consult with an attorney to choose the best option.
4. Obtain a Business License
First, determine the necessary licenses and permits in your target area required to operate as an ISP. This includes permits for the installation and maintenance of network infrastructure. To apply for the license, you may need to visit the office of the local authorities or you may be able to apply online. Furthermore, while applying for the license, you will be required to provide some details related to your business. This includes:
- The name of your business
- What does your business offer?
- How does your business operate?
Usually, it takes around 4-8 weeks to receive a business license.
5. Set Up Infrastructure and Technology
Now you need a wholesale bandwidth provider. So finding the right Internet Provider is the next thing to do. For this, you can do your own research or ask experts for recommendations. Another crucial thing is – The type of network technology you will use. Figure out whether you want to use Fiber optic, Cable, or wireless. This process also demands you to design and deploy your infrastructure.
6. Determine Your Expenses
Estimating the cost is perhaps the most important aspect of business planning. The bandwidth supply service makes up a major part of your expenses. Once that is finalized, it would be wise to estimate the other costs, such as
- Cost of area or room to keep data servers
- Cost of bulk bandwidth
- Cost of hardware/software
- Cost of marketing and sales
- Cost of service
7. Set Up Billing and Payment Systems
For seamless working of your Internet Service Provider Business, it is important to manage customer subscriptions, payments, and invoicing efficiently. A CRM software would be a good choice to track customer information, service requests, and billing. Also, choose a reliable billing system to handle customer payments and billing.
8. Brand and Market Your Services
Create a marketing strategy about how you will reach your target audience. There are several ways through which you can promote your services including ads on local TV, sending flyers, social media marketing, email marketing, etc. Last, but not least, get a website for your business to create a solid brand identity.
9. Ensure Excellent Customer Support
Your customers will be the driving force behind your business. The more happy and satisfied they will be with your service, the more your business will thrive. So make sure you invest time and effort in creating a skillful customer support team. They must ensure that customer queries are resolved as quickly and efficiently as possible.
ISP Glossary: Common Terms Related to Internet Service Providers
In the realm of Internet Service Providers, there are a lot of technical terms that you might come across. Here are some of the most common terms for you to learn about:
1. Bandwidth
It is the capacity of a network to transmit data, measured in bits per second (bps) or megabits per second (Mbps).
2. Router
It is a device that forwards data packets between computer networks, often used to create local networks in homes or businesses.
3. Modem
It is a device modulating and demodulating analog signals, enabling digital devices to communicate over analog telephone lines.
4. IP Address
it is a numerical address assigned to each device connected to a computer network that uses the Internet Protocol for communication.
5. DNS
A system translating human-readable domain names into numerical IP addresses.
6. Packet
A unit of data transmitted over a network, often broken down into smaller packets for efficient transmission.
What is an ISP? Wrapping Up!
Users across the world increasingly rely on the Internet for personal and professional purposes. From all that I have explained above, it is clear that ISPs play a vital role in our modern internet-driven world.
Also, starting an ISP business requires a significant amount of upfront investment in terms of time, money, and resources. According to IBISWorld, there are 27,978 Global Internet Service Providers businesses as of 2024, an increase of 4.4% from 2023. Furthermore, South East Asia (17 businesses), Europe (17 businesses), and North America (15 businesses) are the regions with the most number of Global Internet Service Providers businesses.
It is high time you also start an internet service provider business to meet the growing demand for internet connectivity. Good luck on your entrepreneurial journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
Where do ISPs source their internet connection from?
Tier 1 Service Providers, i.e., the large companies that own and operate extensive global networks of fiber optic cables, are the primary source of internet for ISPs. By purchasing bandwidth from Tier 1 or Tier 2 internet providers, ISPs distribute it to their customers.
How do internet hosting services and ISPs differ?
They serve different purposes. ISPs provide internet access to end users by connecting them to the internet. Acting as a gateway, their role focuses on connectivity and includes handling bandwidth allocation, infrastructure, and routing.
On the other hand, internet hosting services provide hosting infrastructure for websites, applications, and data. Their role is to ensure that websites are accessible to visitors around the world or that website content is available online. The services offered by them include various hosting plans, such as shared hosting, VPS hosting, dedicated hosting, and cloud hosting, to suit different website needs.
How do CDNs speed up content delivery worldwide?
CDNs, or Content Delivery Networks, make use of various strategies to speed up content delivery. This includes caching content at edge servers, routing traffic efficiently, load balancing across servers, employing compression and minification techniques, etc.
What is broadband internet, and what are its key characteristics?
It refers to the high-speed internet that surpasses the traditional dial up connections in terms of speed and availability. Some of the key characteristics of broadband internet include:
- high-speed data transfer (typically starting from 25 Mbps for downloading and 3 Mbps for uploading)
- providing constant access to the internet because of an ‘always-on’ connection
- support for multiple devices simultaneously without any noticeable degradation in performance.
How to Choose the Right ISP?
Two key considerations while choosing the right ISP are reliability and fast internet connection. Consider your typical online activities and look for an ISP that offers download and upload speeds according to your specific requirements. Also, ensure that the ISP offers consistent quality of service and quick customer support. Besides this, you should also compare the costs of different ISPs to choose the one that offers good value for you. Your other considerations may include coverage of the ISP, data caps, contract terms, and customer reviews.
What Information Can an ISP See?
The information visible to ISPs usually includes your browsing history, IP addresses, DNS requests, device information, connection timestamps, data usage, and type of traffic.
What is 5G and how will it impact ISPs?
5G is the latest standard for mobile networks designed to provide significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and higher capacity compared to previous wireless technologies such as 4G, 3G, etc. 5G promises to create new opportunities for ISPs. By incorporating 5G into their offerings, ISPs can provide faster internet services or expand to underserved areas without laying fiber. They can also capitalize on newer services such as IoT applications, autonomous vehicles, and remote surgery. However, 5G also presents challenges for ISPs. The emergence of 5G will increase competition and may force ISPs to lower their prices or improve their services to remain competitive.
What is fiber-to-the-home (FTTH)?
FTTH is a type of broadband internet connection in which fiber optic cables are used directly to residential or business properties. Compared to copper-based connections, FTTH offers several advantages, such as high-speed internet often surpassing 1 Gbps, more reliability, lesser latency, and future-proofing.
Note – This post has been updated on 28-10-2024.