Did you know that “YouTube processes over 500 hours of video every minute”, watched by users on screens of all shapes and sizes? But who is the ‘Behind-the-Scenes’ Magician that makes this seamless playback across devices possible? Let’s give a thought to the famous saying of Steve Jobs – “Technology is nothing. What’s important is that you have faith in people, that they’re good and smart, and if you give them tools, they’ll do wonderful things with them.” Transcoding, indeed, is that tool.
What is transcoding? Probably this is your very next question. In today’s world of digital and online video, transcoding is the technology that ensures that your favorite videos or content streams effortlessly from your phone to your smart TV. In this post, we will help you understand the fundamentals of Transcoding, how it works, and its importance for video streaming. By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of the promising role of this technology in delivering high-quality video content.
What is Transcoding?
Transcoding is the process that converts audio and video files from one format into another. It optimizes the content for different devices so that it is accessible to a wide range of users.
A real-life example will help you understand better. Let’s take a look:
Say, you have a movie file in HD format and you are streaming it on your smart TV. However, your internet connection cannot support streaming large-sized HD files smoothly. This is where the real-time transcoding is performed by the streaming service’s servers. They convert the large movie file into a version they can support. The transcoded version might be in low resolution and is sent to your smart TV. This happens quite quickly ensuring a seamless viewing experience. Transcoding is done using a Transcoder, which in the above example is the server.
Important Terms Related to Transcoding
Often transcoding is confused with various other terms that are related to it, but have different meanings. Let’s understand these terms one by one:
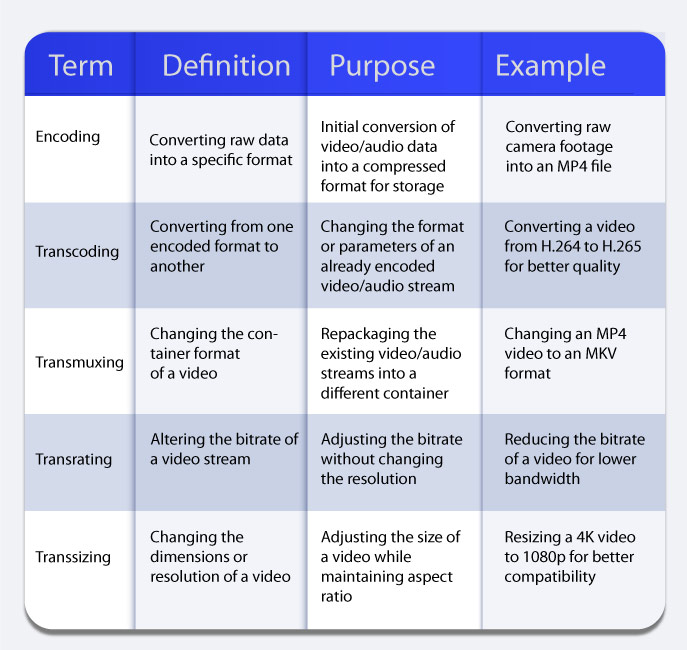
Transcoding vs Encoding
Encoding or compression is compressing and formatting raw media files to convert them into smaller and more transferable versions. Transcoding on the other hand happens after encoding. It is the process where the files are de-encoded, converted into another digital format, and then re-encoded.
Transmuxing
Though transmuxing sounds similar to transcoding, these are different terms. Transmuxing is also termed as ‘Repackaging’, ‘Transcode Multiplexing’, ‘Rewrapping’. Transmuxing is the process of changing the container format of a video file without altering the actual content.
Let’s say you have a video file with an MP4 container format (which contains H.264 video and AAC audio streams). When transmuxing is done, the container format gets changed from MP4 to a different one, like MOV or MKV, while keeping the video and audio streams unchanged. This alteration allows the same content to be compatible with different software or devices without actually changing the content’s encoding.
Transrating
Transrating is also often termed Dynamic Rating. It is the process that involves changing the bitrate of an encoded video stream without altering its original resolution or format. This is done to fit particular files to a much smaller storage space or to adjust the bitrates to optimize file sizes or streaming quality.
For example, let’s consider a high-definition video encoded at a very high bitrate, making it large in file size. By transrating this video, you might create a lower bitrate version of the same video, keeping the resolution intact but reducing the file size significantly. This lower bitrate version would be more suitable for streaming over slower internet connections without compromising resolution. However, it might result in some loss of quality due to the reduced bitrate.
Transsizing

It is the process of resizing the dimensions of frames of a video. The size is changed while maintaining the aspect ratio. It can be increased or decreased based on the specific streaming requirements. For instance, taking a high-resolution video, say in 4K (3840 × 2160 pixels), and transsizing it down to a lower resolution, like 1080p (1920 × 1080 pixels).
Here’s a comparison table of the terms mentioned above for a quick overview:
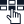
How does Transcoding Work?
Now that we have learned about some of the key terms associated with this process, we shall move to the next section i.e. how does transcoding work? It is a multi-step process as explained below:
The First Step: Decoding
It starts by decoding the original file which is already encoded. The file’s encoded data is broken down into an uncompressed or intermediary format.
Optional Step: Modification
When the file needs to be changed not only in terms of format but also resolution, bitrate, or codec, then this step is also performed. Here the file may be resized, compressed, or altered to the quality of the media.
Second Step: Re-Encoding
The decoded content is then re-encoded into a different format. It works by compressing and reformatting the file. This is in alignment with the specific device or platform where content will be streaming.
Example: Converting a high-resolution video encoded in the AVI format (using the H.264 codec) into a lower-resolution MP4 format (using the HEVC codec) for better compatibility and smaller file size suitable for mobile devices.
Why Transcoding is Essential?
According to the latest online video consumption statistics, 92.3% of internet users worldwide watch digital videos each week. This refers to any kind of video—from music videos and tutorials to gaming and influencer videos.
Transcoding is an essential step in video content delivery. It ensures compatibility across a multitude of devices and resolves challenges related to format compatibility, screen sizes, resolution, and connectivity. We can say that if transcoding is not there then it will be almost impossible to enjoy seamless playback experiences. With the speed at which media consumption is evolving, this technology certainly becomes a necessity to ensure that content reaches and engages a broad audience while maintaining quality.
Different Types of Transcoding
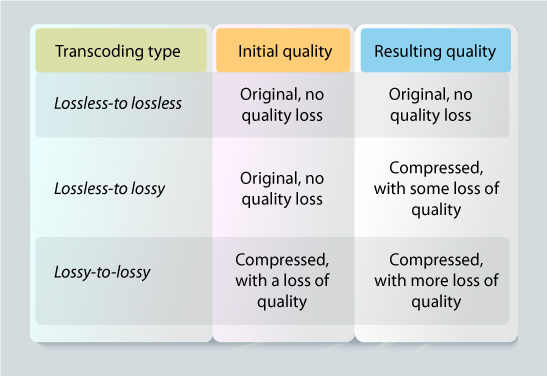
Lossy To Lossy
As the term suggests, this type of transcoding produces the lowest-quality audio or video files. This happens because you already have a low-quality file which when transcoded further lowers its quality. It lowers the bitrate and results in poor quality. However, quality is sacrificed because it saves storage space on portable devices such as tablets and smartphones. This type of compression technique is used only in cases when files of smaller sizes are required.
Lossless To Lossless
In this type, there is no loss of data quality. So when compression is done on an audio or video file, the quality remains the same. This is appropriate when you want to convert a file to a different format without compromising the quality. Lossless to Lossless transcoding implements better compression and good quality hardware to perform its functioning. However, the resulting files are often large in size, making them unsuitable for smaller or portable devices.
Lossless To Lossy
Compared to lossy-to-lossy, this technique results in lesser degradation of quality when compressed. Though the resulting files in lossless-to-lossy are not as good in quality as lossless-to-lossless, they are small enough in size to be stored and accessed on portable devices. This is the reason why it is the most popular form of transcoding. It is important to note that once a file is compressed via lossless-to-lossy, the lost data cannot be retrieved.
Now you may be wondering whether there is a transcoding technique like lossy-to-lossless. The answer is no. There is no such transcoding.
5 Use Cases of Transcoding
Now we will take a look at some real-life instances where transcoding plays a crucial role.
Streaming Services (Netflix and Amazon Prime)
Netflix had around 247.2 million paid subscribers worldwide as of the third quarter of 2023. Imagine the amount of content consumed through this platform every single day. Such platforms use transcoding to convert high-resolution content into different formats that are suitable for streaming on devices with varying screen sizes and internet speeds. Netflix uses codecs like H.264/AVC or H.265/HEVC for transcoding. They also employ adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) protocols like MPEG-DASH or HLS to deliver varying-quality streams.
Social Media Platforms ( YouTube and TikTok)
With content consumption as crazy as a whirlwind, social media platforms like YouTube and Instagram also utilize transcoding using codecs like VP9 or H.264. to convert user-uploaded videos into suitable (1080p, 720p) and formats (MP4, WebM). Thus ensuring smooth and seamless playback across a wide range of devices like smartphones, tablets, and smart TVs.
Live Broadcasting (Television Networks)
Live TV Broadcasting is the new frontier of instantaneous, interactive, and immersive content delivery. These services transcode live broadcasts by using MPEG-2, H.264, or H.265 codecs to ensure compatibility across varying devices and network conditions. Protocols like RTMP or HLS are employed for delivering live streamsSeamless streaming of sports matches and live concerts.
Cloud Storage Services (Google Drive and DropBox)
Google Drive has more than 2 billion active monthly users and more than 2 trillion files in its database, including videos, images, documents, etc. Behind these mind-blowing numbers lies the pivotal role of Transcoding. Cloud Storage services transcode uploaded videos to multiple formats, enabling users to stream or download files across various devices. Google Drive and Dropbox use codecs like H.264 or VP9 for transcoding
Mobile Applications (WhatsApp and Messager)
Transcoding is used by mobile applications to compress and optimize video content before sending them. Some common codecs used in mobile applications for transcoding are H.264 (AVC) (widely supported), H.265 (HEVC) (offers better comp[ression but not universally supported), VP9 (developed by Google), AAC (used for audio compression).
Benefits of Transcoding
Transcoding offers several benefits to both streamers and viewers. Here’s the explanation for each side:
Transcoding Benefits for Streamers
-
Supports Multiple Formats
These days users have access to a wide array of devices and require different video formats. Encoding video files into different resolutions and bitrates can be a daunting task given the the large volume of viewership. Transcoding eliminates the incompatibility barriers and ensures successful streaming. It does so by delivering appropriately compressed files to users in a relatively short time and low cost for the streamers.
-
Optimized Content Quality
Streamers want to maintain control over the quality of their content across diverse platforms and devices. Transcoding enables them to optimize the same by delivering the best possible quality without compromising on user experience.
-
Increased Reach and Accessibility
Poor internet speed often limits users from viewing content. While in many parts of the world, users have access to high-speed internet and can view content just like that. But there are regions where internet speed is quite low and streaming online videos takes time. Transcoding solves this problem by offering content in various formats and qualities, ensuring that viewers with different devices and internet speeds can access their streams.
Transcoding Benefits for Viewers
-
Adaptive Streaming
Transcoding supports adaptive streaming i.e. it adjusts the video quality in real-time. This is particularly beneficial for viewers with varying internet speeds and who dynamically switch between devices with different resolutions.
-
Less Buffering
Viewers with poor internet bandwidth can immensely benefit from transcoding or areas where network congestion happens. Transcoding provides multiple bitrates and resolutions, thus minimizing buffering during streaming.
-
Improved Accessibility
A significant advantage of using transcoding is that closed captions and subtitles can be added as the transcoding process happens. Even alternative audio tracks can be transcoded into videos which expands the accessibility of the content to a broader audience.
How Can you Transcode your Videos?
Transcoding is accomplished with the help of a transcoder which could be in the form of a streaming server or a cloud-based transcoding platform. There are 3 ways in which you can transcode your videos. Let’s take a look at each one of them:
Using Video Platforms
One of the simplest ways is to use a video platform for transcoding. You just need to upload your video and the platform will create multiple qualities of the video. These services usually charge some fee for this conversion. With this option, you have no control over quality and price.
Go for On-Premise Transcoding
Building your own transcoder can also be a good option if you want to have complete control over the cost and quality. You can purchase or rent servers, install transcoding software, and do video processing in-house. In this model, you get the flexibility to customize transcoding settings as per your requirements. It is suitable for large-scale processing.
Leverage Cloud-based Transcoding Services
This is another good option when you don’t want to deal with the complexities of the transcoding process. Simply choose a reliable cloud transcoding service, upload your video, and set the desired parameters. Once completed, you can download the transcoded file. The pricing structure of cloud services is often based on factors like file size, duration, and resolution.
The biggest advantage of cloud services is that they are highly scalable and cost-effective. Some useful and popular cloud-based transcoding services are Amazon Elastic Transcoder, Azure Media Services, and ImageKit.
5 Best Practices for Video Transcoding
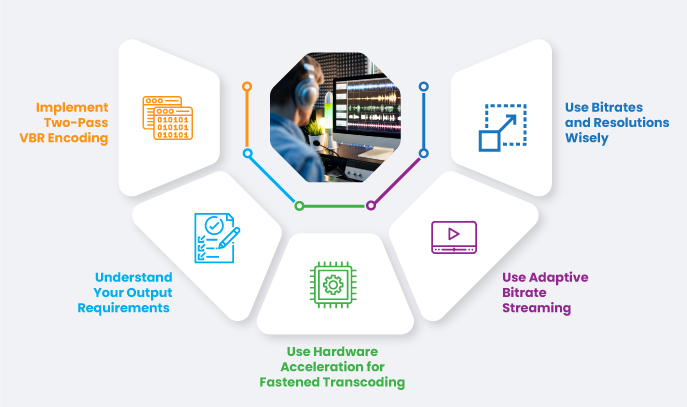
The ultimate goal behind any video transcoding process is to deliver high-quality content that’s compatible across diverse platforms and devices. One must adhere to some best practices for video transcoding to achieve this goal. Here are the 5 most useful ones:
Implement Two-Pass VBR Encoding
Variable Bitrate Encoding allows the bitrate of video content to change dynamically adapting to the complexity of the video every single second. This results in a higher quality of video content at a smaller file size. The process of 2-Pass VBR encoding involves 2 steps –
- In the first pass, the video content is analyzed to determine a suitable bitrate
- In the second pass, the video is encoded based on the information gathered in the first step.
2-pass VBR Encoding ensures smooth playback by adjusting the quality based on the viewer’s internet speed.
Understand Your Output Requirements
When producing video content, it is important to know your audience and the devices where your content will be viewed. Accordingly, you should research the technical specifications and the recommended settings such as video formats, codecs, resolutions, and bitrates for the target platforms and devices.
Use Hardware Acceleration for Fastened Transcoding
Hardware accelerators are specialty-designed hardware components such as GPUs and DSPs that expedite the process of video transcoding. The process works by offloading some specific tasks to the hardware components (like some calculations that can perform better than the CPU). This results in improved efficiency across the board. Make sure to check the compatibility of the hardware with the software beforehand.
Use Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Also called ABR, it allows the video content to adapt to the varying network conditions in real-time. This helps in optimizing the viewing experience of the users. In the ABR technique, the video gets broken into small segments and each segment is encoded into multiple quality levels. For each segment, an appropriate quality level is selected as per the user’s current network conditions.
Use Bitrates and Resolutions Wisely
Your choice of bitrate and resolution will decide the balance between the quality of the video and file size. Therefore keep in mind the type of content and your target audience when selecting the bitrate and resolution. Suppose you are streaming high-motion video content, then you should certainly go for a higher bitrate and resolution so that details are captured. When it comes to static scenes, a lower bitrate and resolution will work just fine.
Pro Tip – Avoid scaling up and streaming at a higher resolution than your original video source. For instance, the capturing is at 720p and you decide to stream at 1080p. It will not enhance the quality, rather you will end up using more bandwidth than is necessary for you and your viewers.
Considerations for Choosing a Transcoding Service
With all that we have learned now about transcoding, the obvious question that comes to mind is – How to choose the best transcoding service? Let’s make the job easy for you. Just consider these 2 aspects when you are selecting the ideal transcoding service:
- Decide Between a Cloud Solution and a Software
If you want things to be simpler, more secure and to work faster, then opting for a cloud transcoding solution (hosted in the cloud) might be the better choice. However, if you have a private network with suitable infrastructure, then transcoding software would be the ideal fit for you.
- Consider the Type of Digital Media You are Transcoding
A language translator understands different languages each of those having their own words and rules and converts them into different languages understood by the recipient. Transcoding works similar to that of a translator but for media files. Just like languages, audio, and video files have their own types and rules. A good translator should be versatile enough to handle different types of audio and video files.
Key Takeaway
Hopefully, I have covered most of your questions regarding transcoding, especially if you are a beginner in the field of video streaming. The number of digital video viewers worldwide is expected to reach 3.5 billion. In 2023, people are watching, on average, 17 hours of online videos per week. With these statistics, it is evident that the role of Transcoding is certainly revolutionizing video consumption and delivery.